Patagonian red octopus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Patagonian red octopus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Cephalopoda |
| Order: | Octopoda |
| Family: | Enteroctopodidae |
| Genus: | Enteroctopus |
| Species: |
E. megalocyathus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Enteroctopus megalocyathus (Gould, 1852)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Patagonian red octopus is a fascinating sea creature. Its scientific name is Enteroctopus megalocyathus. People in Chile call it "Pulpo del sur," and in Argentina, it's known as "Pulpo colorado." This octopus is a medium-sized member of the Enteroctopus family.
Contents
What Does It Look Like?
The Patagonian red octopus is quite big, but not as huge as some other giant octopuses. For example, it's smaller than the famous Giant Pacific octopus.
Most Patagonian red octopuses weigh about 4 kilograms (about 9 pounds). Some can grow even larger, up to 7.5 kg for males and 8 kg for females. Their body, called the mantle, can be about 22.5 centimeters (9 inches) long. When you include their arms, they can stretch over 1 meter (3 feet) long. Some have even been seen reaching 1.3 meters (over 4 feet) in total length!
Like other octopuses in its family, this octopus has special features. Its body has long folds and grooves. It also has large, paddle-like bumps called papillae.
Where Does It Live?
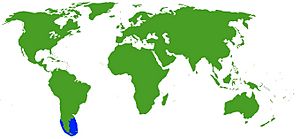
This octopus lives along the southeastern coast of South America. You can find it in the waters off Argentina in the Atlantic Ocean. It also lives off the coast of Chile in the Pacific Ocean.
In Chile, its home ranges from northern Patagonia down to the Strait of Magellan. It can even be found as far south as 56°S latitude. In Argentina, it lives from the San Matías Gulf to the Beagle Channel. This includes the Falkland Islands and the Burdwood Bank.
You can find these octopuses in different depths of water. Young octopuses might live in shallow, rocky areas near the shore. Adults can be found much deeper, sometimes up to 220 meters (about 720 feet) below the surface.
What Does It Eat?
The Patagonian red octopus is an opportunistic predator. This means it eats whatever food it can find easily. Its diet includes crabs, fish, and other molluscs. It enjoys eating clams, mussels, and sea snails.
In southern Chile, adult octopuses love to eat large crabs. They might even eat other Patagonian red octopuses, as they can be cannibalistic. Younger octopuses have a slightly different diet. They prefer smaller crabs, crab eggs, shrimp, and squat lobsters.
Who Eats the Octopus?
Like many octopuses, the Patagonian red octopus is a tasty meal for bigger animals. Several predators hunt this octopus.
Some of its main predators include beaked skates, which are a type of flat fish. Spiny dogfish, a kind of shark, also enjoy eating them. The South American sea lion is another animal that often hunts and eats the Patagonian red octopus.
Fishing for Octopuses
The Patagonian red octopus is important for fishing in Chile. It is one of two main octopuses caught there for food. The other is Octopus mimus. Each year, between 2,000 and 5,000 tons of these two octopuses are caught.
To protect the octopus population, there are rules for fishing. In Chile, it is against the law to catch them from October 15 to March 15. This ban helps the octopuses reproduce and grow. During the regular fishing season, only octopuses weighing more than 1 kilogram (about 2.2 pounds) can be caught.
See also
 In Spanish: Pulpo rojo patagónico para niños
In Spanish: Pulpo rojo patagónico para niños