Plastic bag ban facts for kids
Have you ever gone to a store and had to pay for a plastic bag, or been told they don't have them at all? This is because of a plastic bag ban or charge, a type of law that limits how stores can use lightweight plastic bags. Around the world, more and more places are getting rid of these single-use bags.
For a long time, stores gave out free plastic bags made from a material called low-density polyethylene. People thought they were a handy, cheap, and clean way to carry things home. But these thin bags, which are less than 50 microns thick (thinner than a human hair), cause big problems for our planet. They are made from non-renewable resources like oil and gas, and they create a lot of pollution. To help solve this, many stores now encourage people to use reusable shopping bags instead.
Governments have tried different ways to fix the problem. Some have completely banned the sale of lightweight bags. Others make stores charge customers a small fee for each bag. Bangladesh was the first country to ban these bags back in 2002. Since then, over 127 countries have created rules to reduce plastic bag use.
Contents
Why Are Plastic Bags a Problem?
Plastic bags create many problems for the environment. One of the biggest issues is the huge amount of waste they become. Many bags end up as litter on our streets. From there, they can blow into rivers and oceans, polluting the water.
Even when thrown away correctly, plastic bags take hundreds of years to decompose or break down. This means they pile up in landfills. When they get into nature, they can clog sewers and harm wildlife. Every year, tons of plastic waste ends up in the ocean. This threatens sea creatures and messes up the marine food chain.
Harm to Wildlife
Animals can get tangled in plastic bags, which can cause them to drown. They also often mistake plastic bags for food. When an animal eats a plastic bag, it can block its stomach and intestines, leading to starvation.
The World Wide Fund for Nature estimates that over 100,000 whales, seals, and turtles die each year from eating or being trapped by plastic bags. In India, about 20 cows die every day from eating plastic bags. In parts of Africa, clogged sewers from plastic bags create breeding grounds for mosquitoes, which can lead to more cases of malaria.
Climate Change and Pollution
Plastic bags also contribute to climate change. When plastic is left out in the sun, it releases greenhouse gases like methane and ethylene. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere and warm the planet.
Plastic bags don't biodegrade (break down naturally). Instead, they just break into smaller and smaller pieces. These tiny pieces can release harmful chemicals into the soil and water. These toxins can affect the bodies of animals and humans. A single plastic bag might only be used for about 20 minutes, but it can pollute the environment for many years.
How Do We Reduce Plastic Bag Use?
There are a few main ways that governments try to phase out lightweight plastic bags. Charges and bans are the most common methods.
Charging for Bags
One popular method is to charge a small fee for each plastic bag. This includes taxes or fees that customers have to pay at the store. As of 2024, 30 countries have this kind of charge. This method reduces plastic bag use and also raises money that can be used for environmental projects. It also lets people choose to pay for a bag if they really need one.
Banning Bags
A ban is a strict rule that stops stores from giving out single-use plastic bags. As of 2024, 27 countries have a full ban. While this is a very direct way to stop people from using thin bags, it can have a downside. Sometimes, people just start using thicker plastic bags that aren't banned, and they still throw them away.
Taxing Manufacturers
Instead of making customers pay, some countries tax the companies that make the plastic bags. This puts the responsibility on the producers. Some laws also require companies to help pay for recycling programs. This encourages them to design bags that are better for the environment.
Recycling
Recycling plastic bags seems like a good idea, but it's not a perfect solution. Only about 5% of plastic bags are actually recycled. They can easily blow away from recycling bins and become litter. Also, different types of plastic bags can't be recycled together and can jam the machines at recycling centers.
Do These Rules Actually Work?
Yes, rules against plastic bags have been very successful in many places. After a charge is introduced, the number of bags people use often drops quickly.
- In Ireland, a plastic bag tax in 2002 led to a 90% drop in bag use almost overnight.
- In Portugal, a similar tax in 2015 also caused a big decrease in plastic bag use.
- In Seattle, USA, a ban led to 50% fewer plastic bags in the city's waste, even as the city's population grew.
- In Kenya, a 2017 ban was supported by most people, who said they saw cleaner streets and less waste.
However, sometimes there are unexpected results. In California, a ban on thin plastic bags led to more people buying thicker plastic bags. These thicker bags create even more plastic waste if they are not reused many times. This shows that how a law is designed is very important for it to be successful.
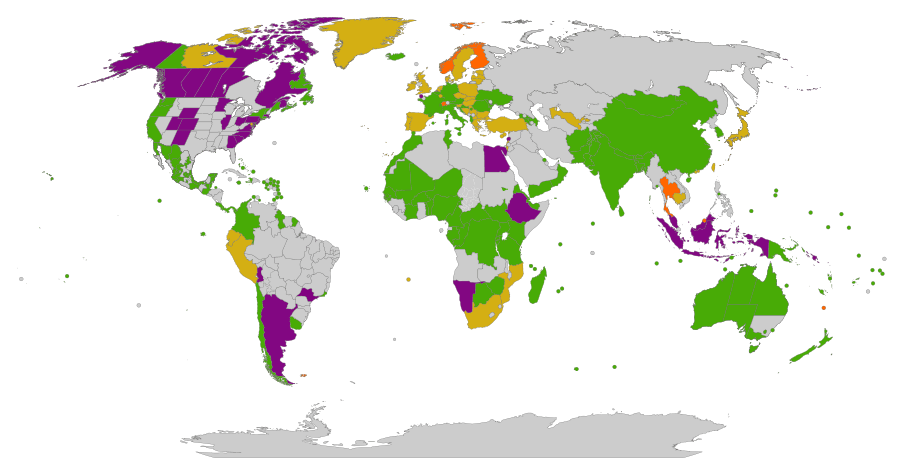
Rules Around the World
Many countries have taken action against plastic bags. The map above shows a summary of these laws. Green countries have a ban, yellow countries have a charge, and purple countries have rules in certain cities or regions.
Africa
Many African nations have some of the strictest plastic bag bans in the world.
- Kenya banned single-use plastic bags in 2017. Anyone caught making, selling, or using them can face large fines or even jail time. In 2020, the country also banned single-use plastics in protected areas like national parks and beaches.
- Rwanda banned plastic bags back in 2008. The country is known for being very clean, partly because of this rule.
- Tanzania put a nationwide ban on plastic bags into effect on June 1, 2019.
Asia
- Bangladesh was the first country in the world to ban thin plastic bags in 2002. This happened after plastic bag litter clogged drainage systems and made major floods worse.
- China introduced a fee for plastic bags in 2008 and banned the thinnest bags. This greatly reduced bag use in supermarkets. The country has since moved toward a full ban.
- India has had rules against thin plastic bags since 2002. Many states and cities have their own, stricter bans because the national rule was not always followed.
Europe
The European Union passed a rule in 2015 to cut plastic bag use. Member countries can choose how to do this, either with a ban or a charge.
- Ireland was a pioneer in Europe. Its 2002 plastic bag tax was a huge success, cutting bag use by 90%. The money from the tax goes into an environmental fund.
- Germany banned all single-use plastic shopping bags starting in 2022.
- The United Kingdom introduced a 5p charge for bags in England in 2015, which has cut bag use by over 97% in major supermarkets. Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland have similar successful charges.
North America
- Canada banned the manufacture and import of single-use plastic bags in December 2022.
- The United States does not have a national ban. However, several states, including California, New York, and New Jersey, have banned disposable bags. Many cities and counties across the country also have their own bans or fees. In 2024, California passed a law to ban all plastic bags statewide by 2026.
- Mexico has banned plastic bags in many of its states, including Mexico City.
Oceania
- Australia does not have a national ban, but all of its states and territories have banned lightweight plastic bags. After the two largest supermarket chains stopped giving out free bags, plastic bag use dropped by 80% in just three months.
- New Zealand phased out single-use plastic bags in 2019. The government has also banned other plastic items like straws and cutlery.
South America
- Chile became the first country in Latin America to ban plastic bags nationwide in 2018. The law was phased in, starting with large stores and later including small shops.
- Colombia introduced a tax on plastic bags in 2017 to discourage their use.
- Uruguay banned all non-biodegradable plastic bags in 2019.
See also
 In Spanish: Eliminación de las bolsas de plástico ligeras para niños
In Spanish: Eliminación de las bolsas de plástico ligeras para niños
- Biodegradable bag
- Phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles
- Phase-out of incandescent light bulbs
- Sustainability
- Waste management
- Reusable shopping bag