Planetary differentiation facts for kids
Planetary differentiation is a super cool process that happens inside planets and other space objects! It's how a planet sorts itself out into different layers, kind of like how oil and water separate in a glass. The heavier stuff sinks to the middle, and the lighter stuff floats to the top. This is how planets get their different parts, like a core, a mantle, and sometimes a crust on the outside. This has happened on Earth, the Moon, and even some asteroids!
Contents
What is Planetary Differentiation?
Planetary differentiation is a natural process where a planet or a similar space body separates into distinct layers. Think of it like a giant mixing bowl of ingredients that slowly settles. The densest, heaviest materials move towards the center. Meanwhile, the lighter materials rise up towards the surface. This process is how planets develop their layered structure.
How Planets Form Layers
When a planet first forms, it's often a mix of different materials. These materials can be hot and melted, or they can be a mix of solid and melted rock. Over time, the force of gravity pulls everything towards the center of the planet. But not all materials are pulled equally. Heavier, denser materials are pulled more strongly and sink deeper. Lighter, less dense materials are pushed upwards.
Why Does This Happen?
This layering happens mainly because of two things:
- Density: Different materials have different densities. For example, iron is much denser than rock.
- Heat: Early planets were very hot, often hot enough to melt their insides. When materials are melted, they can move around more easily. This allows the denser materials to sink and the lighter materials to rise. It's like how bubbles rise in a boiling pot of water.
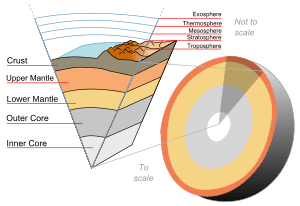
What Are These Layers?
This process usually creates at least two main layers:
- Core: This is the innermost layer. It's made of the densest materials, often metals like iron and nickel. Earth has a solid inner core and a liquid outer core.
- Mantle: This layer surrounds the core. It's made of less dense rock than the core. On Earth, the mantle is mostly solid but can flow very slowly over long periods.
- Crust: Sometimes, the lightest materials form a thin, solid outer layer called the crust. This is the part we live on!
Where Do We See Differentiation?
Planetary differentiation has happened on many different space objects.
- Planets: Earth, Mars, Venus, and Mercury all show clear signs of differentiation with cores, mantles, and crusts.
- Dwarf Planets: Even smaller bodies like Pluto and Ceres are thought to have differentiated.
- Moons: Earth's Moon and Jupiter's moon Io are good examples of differentiated natural satellites.
- Asteroids: Some large asteroids, like 4 Vesta, also show evidence of having distinct layers.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Diferenciación planetaria para niños
In Spanish: Diferenciación planetaria para niños