Population facts for kids
Population is a word that means the total number of people living in a certain area. For example, the population of your town is how many people live there. Governments often count their population using a special survey called a census.
The word "population" isn't just for people! It can also refer to the number of animals, tiny living things, or plants in an area. Scientists who study nature, like in ecology (the study of how living things interact with their environment), use this word a lot.
Contents
What Does 'Population' Mean?
The word "population" comes from an old Latin word, populus, which means "a people." So, it literally means "a group of people."
How Many People Are in the World?
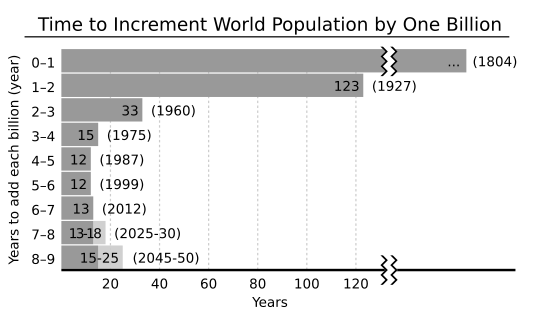
The world's human population is always changing! The United Nations (UN) reported that on November 15, 2022, there were more than 8 billion people on Earth. That's a huge jump from October 2011, when the population reached 7 billion.
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) says that having so many people brings both big challenges and exciting chances for everyone. The United States Census Bureau also keeps track. They estimated that the world population reached 6.5 billion on February 24, 2006.
It's hard to get an exact number for the world's population. Some countries, like Nigeria, don't even know their population to the nearest million. This means there's always a bit of guesswork in these big numbers.
One researcher, Carl Haub, figured out that over 100 billion people have probably been born in the last 2,000 years!
How Will the World's Population Change?
The world's population started growing much faster after the Industrial Revolution began around 1700. In the last 50 years, the growth has been even quicker. This is thanks to amazing medical advances and big improvements in farming. The "Green Revolution" in the 1960s helped farmers grow much more food.
The United Nations thinks the world's population will reach about 9.8 billion by 2050. They also predict it could be around 11.2 billion by the year 2100.
Some experts believe the world's population might stop growing and even start to shrink before the end of this century. This could happen for several reasons. These include economic changes, health concerns, and environmental issues. For example, some countries in Eastern Europe have already seen their populations decline in recent years.
In many less-developed parts of the world, the number of births has slowly gone down. This happened after the number of deaths dropped sharply. This shift, from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates, is called the demographic transition.
Planning for Population Growth
Human population planning is about trying to change how fast a human population grows. In the past, people often focused on slowing down population growth. From the 1950s to the 1980s, there were worries about how fast the global population was growing. People thought it might cause more poverty, harm to the environment, and political problems.
These efforts aimed to reduce growth rates. While some programs helped people have more control over their own families, a few programs used strict rules. For example, China had a "one-child per family" policy for a long time.
By the 1970s, there was a disagreement between those who wanted to control population and those who wanted to protect women's reproductive rights. People started to believe that women should have the right to make choices about their own bodies and families. This led to big changes in population policies in the early 1980s, focusing more on human rights.
See also
 In Spanish: Población para niños
In Spanish: Población para niños
- Community (ecology)
- Human overpopulation
- List of countries by population
- Lists of organisms by population
- Population ethics
- Population geography
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |