Privateer facts for kids
A privateer was like a special kind of ship that was owned by regular people, not the government. But during a war, the government would give these ships a special paper called a Letter of Marque. This paper allowed them to attack and capture enemy ships and their goods. It was a way for countries to add more ships to their fighting force without having to pay for them directly.
Well known privateers include Sir Francis Drake and Martin Frobisher.
Contents
What Was a Privateer?
A privateer was a privately owned ship that acted a bit like a warship during times of conflict. Unlike pirates, privateers were legal. They had permission from their government to attack enemy ships. This permission came in the form of a special document called a Letter of Marque. This letter made their actions legal under international law at the time.
How Privateers Operated
When a country was at war, it might not have enough warships to fight all its enemies. This is where privateers came in handy. The government would issue a Letter of Marque to a ship owner. This letter allowed the privateer to capture enemy merchant ships and their cargo. The privateer crew would then sell the captured goods and share the profits. This system helped the government by disrupting enemy trade and adding more ships to their side without direct cost.
Privateers in American History
Privateers played an important role in the early history of the United States.
American Revolution
During the American Revolution, American privateers were very active. They raided British shipping, which helped to disrupt the British war effort. These attacks made it harder for Britain to supply its troops and trade with other countries.
War of 1812
Privateers were used again during the War of 1812 against Great Britain. American privateers once more attacked British merchant ships. This put pressure on the British economy and helped the American war effort.
American Civil War
Later, during the American Civil War, the CSA also issued Letters of Marque. They used privateers to try and break the naval blockade set up by the Union (the United States).
Images for kids
-
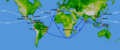
16th-century trade routes prey to privateering: Spanish treasure fleets linking the Caribbean to Seville, Manila-Acapulco galleons started in 1568 (white) and rival Portuguese India Armadas of 1498–1640 (blue)
-
Woodes Rogers' men search Spanish ladies for their jewels in Guayaquil, 1709
-
An action between an English ship and vessels of the Barbary corsairs
-
Bermuda Gazette of 12 November 1796, calling for privateering against Spain and its allies during the 1796 to 1808 Anglo-Spanish War, and with advertisements for crew for two privateer vessels.
-
A Bermuda sloop engaged as a privateer.
-
The Spanish Amaro Pargo was one of the most famous corsairs of the Golden Age of Piracy.
See also
 In Spanish: Corsario para niños
In Spanish: Corsario para niños