Prosencephalon facts for kids
| Brain: Forebrain (Prosencephalon) | ||
|---|---|---|
Quick facts for kids
|
||
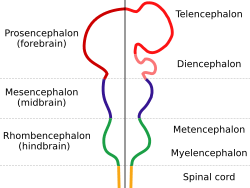
| Diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. These regions will later differentiate into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain structures. |
The forebrain, also called the prosencephalon (say: pro-sen-SEF-uh-lon), is a very important part of your brain. It's one of the three main sections that your brain develops into, right from when you are a tiny embryo. The other two main parts are the mesencephalon (midbrain) and the rhombencephalon (hindbrain).
The forebrain helps you do many amazing things. It's where you think, learn, remember, and feel emotions. It also helps you control your movements and understand what your senses are telling you.
Sometimes, during early development, the forebrain might not divide into two halves as it should. This can lead to a condition called holoprosencephaly.
Contents
What the Forebrain Does
The forebrain is like the control center for many of your most complex actions and thoughts. It helps you with things like:
- Thinking and Problem-Solving: When you figure out a math problem or plan your day, your forebrain is hard at work.
- Memory: Remembering what you learned in school or what you had for breakfast uses your forebrain.
- Emotions: Feeling happy, sad, or excited all involves different parts of your forebrain.
- Senses: It processes information from your eyes, ears, nose, and skin, helping you understand the world around you.
- Movement: It helps you decide to move your arm or leg and then sends the signals to make it happen.
Main Parts of the Forebrain
The forebrain is made up of two main sections: the telencephalon and the diencephalon. Each of these has even smaller, specialized parts.
The Telencephalon: Your Thinking Cap
The telencephalon (say: tel-en-SEF-uh-lon) is the largest part of the forebrain. It develops into the cerebrum, which is the biggest part of your entire brain. The cerebrum is divided into two halves, called hemispheres.
The Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the wrinkled, outer part of your brain that you often see in pictures. It's responsible for your higher-level thinking.
- Cerebral Cortex: This is the outer layer of the cerebrum. It's where most of your conscious thoughts happen. It's divided into different areas, each with special jobs. For example, one part helps you see, another helps you hear, and another helps you speak.
- Basal Ganglia: These are groups of cells deep within the cerebrum. They help control your movements and make them smooth and coordinated.
- Limbic System: This system is involved in your emotions, memory, and motivation. It includes parts like the hippocampus (important for forming new memories) and the amygdala (involved in processing emotions like fear).
The Diencephalon: The Brain's Relay Station
The diencephalon (say: dy-en-SEF-uh-lon) is located deep inside the brain, between the cerebrum and the midbrain. It acts like a relay station, sending messages between different parts of the brain and the rest of the body.
The Thalamus
The thalamus (say: THAL-uh-mus) is a major relay center. Almost all sensory information (like what you see, hear, or touch) goes through the thalamus before it reaches the cerebral cortex. It helps to filter and direct these messages to the right places in your brain.
The Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (say: hy-po-THAL-uh-mus) is a small but very powerful part of the diencephalon. It controls many important body functions that you don't even have to think about.
- Body Temperature: It helps keep your body at the right temperature.
- Hunger and Thirst: It tells you when to eat and drink.
- Sleep Cycles: It helps regulate your sleep and wake patterns.
- Hormones: It controls the release of many hormones from the pituitary gland, which affect growth, metabolism, and stress responses.
Development of the Forebrain
The forebrain starts to form very early in an embryo's life. It begins as a simple tube that then swells and divides into different sections. These sections grow and fold, eventually forming the complex structures of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. This amazing process of development is what allows us to have such advanced thinking abilities.
See also
 In Spanish: Prosencéfalo para niños
In Spanish: Prosencéfalo para niños