RGB facts for kids
RGB is a way to create colors using light. It's often called additive color mixing because you add different colored lights together to make new colors. The three main colors used are red, green, and blue.
You see RGB colors every day on screens like your TV, computer, or phone. These screens have tiny red, green, and blue lights (or pixels) that glow. When these lights mix together, they can create millions of different colors.
For example, if you mix red light and green light, you get yellow. If you mix all three colors – red, green, and blue – at their brightest, you get white light. If all three are off, you get black.
Computers often use a special code called a hexadecimal code to represent RGB colors. This code looks like `#RRGGBB`. The first two letters (`RR`) tell the computer how much red light to use. The next two (`GG`) are for green, and the last two (`BB`) are for blue. Each color can have a value from 0 (no light) to 255 (full brightness). So, `#FF0000` would be pure red (full red, no green, no blue), and `#00FF00` would be pure green.
Contents
How RGB Works
RGB works by shining different amounts of red, green, and blue light. When these lights hit your eyes, your brain mixes them together to see a specific color. This is different from mixing paints, which is called subtractive color mixing. With paints, you start with white and remove colors. With light, you start with black (no light) and add colors.
Making Colors with Light
Imagine you have three flashlights, one with a red filter, one with a green filter, and one with a blue filter.
- If you shine just the red light, you see red.
- If you shine the red and green lights on the same spot, you'll see yellow.
- If you shine the green and blue lights, you'll see cyan (a blue-green color).
- If you shine the red and blue lights, you'll see magenta (a purplish-red color).
- When you shine all three lights together, you get white light.
This is how your screen creates all the colors you see. Each tiny spot on your screen has red, green, and blue parts that can glow at different brightness levels.
RGB in Digital Images
When you take a picture with a digital camera or create an image on a computer, the colors are often stored using the RGB model. Each pixel in the image has information about how much red, green, and blue it needs to show. This information is then used by your screen to display the correct color.
For example, a bright yellow pixel might be stored as a mix of full red and full green light, with no blue. A dark blue pixel would have a low amount of blue light and no red or green.
Where is RGB Used?
RGB is super important in anything that uses light to show colors.
Computer Screens and TVs
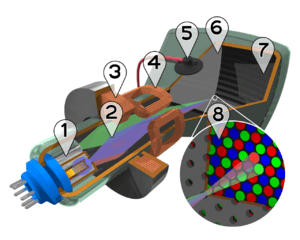
Almost all modern computer monitors, televisions, and smartphone screens use the RGB color model. They have tiny red, green, and blue sub-pixels that light up to create the images you see.
Digital Cameras and Scanners
When you take a photo with a digital camera, it captures light using sensors that are sensitive to red, green, and blue. The camera then combines this information to create a full-color image. Scanners work in a similar way to capture images from paper.
Web Design
If you've ever seen a website designer pick a color, they often use RGB values or hexadecimal codes. This tells the web browser exactly what color to display for text, backgrounds, or images.
Images for kids
-
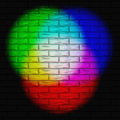
Additive color mixing: projecting primary color lights on a white surface shows secondary colors where two overlap; the combination of all three primaries in equal intensities makes white.
-
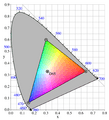
A set of primary colors, such as the sRGB primaries, define a color triangle; only colors within this triangle can be reproduced by mixing the primary colors. Colors outside the color triangle are therefore shown here as gray. The primaries and the D65 white point of sRGB are shown. The background figure is the CIE xy chromaticity diagram.
See also
 In Spanish: RGB para niños
In Spanish: RGB para niños