Rectifier facts for kids
A rectifier is a special electronic device that changes Alternating current (AC) into Direct current (DC). This process is called rectification. Think of it like this: AC electricity constantly changes direction, flowing back and forth, while DC electricity always flows in one direction. Rectifiers are super important because many electronic devices, like your phone charger or computer, need steady DC power to work, even though the power from wall outlets is usually AC.
Rectifiers are often made from materials like copper, iron, and silver. They are key parts in many everyday electronics, from radios to televisions and even in the systems that charge your car battery.
Contents
How Rectifiers Work: AC to DC
Imagine electricity as water flowing through pipes.
- Alternating Current (AC) is like water sloshing back and forth in a pipe. It changes direction many times a second. This is how electricity travels from power plants to your home.
- Direct Current (DC) is like water flowing steadily in one direction through a pipe. Most electronic gadgets, like batteries, use DC.
A rectifier acts like a special valve that only lets the electricity flow in one direction. It takes the "back and forth" AC and turns it into "one-way" DC.
Types of Rectifiers
There are two main types of rectifiers:
Half-Wave Rectifiers
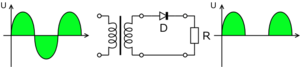
A half-wave rectifier is the simplest type. It only uses one half of the AC waveform. When the AC current flows in one direction, the rectifier lets it through. But when the AC current tries to flow in the opposite direction, the rectifier blocks it. This means you only get pulses of electricity flowing in one direction, like taking only the "forward" pushes of the water and ignoring the "backward" pulls. It's not a very smooth DC, but it works for some simple uses.
Full-Wave Rectifiers
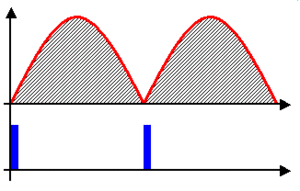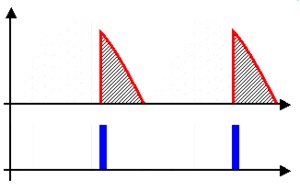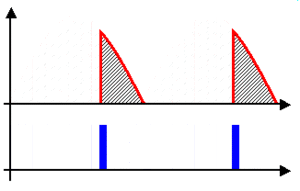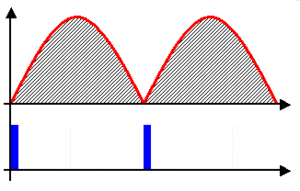
A full-wave rectifier is more advanced. It uses both halves of the AC waveform to create DC. Instead of just blocking one half, it flips the "backward" half of the AC current so it also flows in the "forward" direction. This creates a much smoother and more continuous flow of DC electricity.
One common way to make a full-wave rectifier is by using a diode bridge.
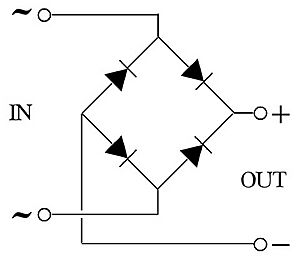
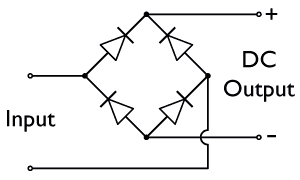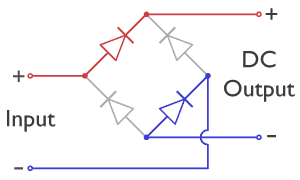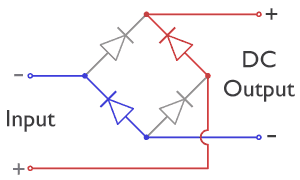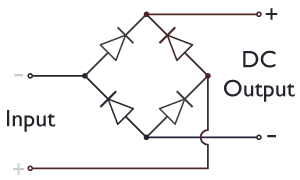
What is a Diode Bridge?
A diode bridge is an electrical circuit made up of four diodes. A diode is a tiny electronic component that acts like a one-way valve for electricity, letting it flow in only one direction.
When AC electricity enters a diode bridge, the four diodes work together to steer the current. No matter which way the AC current tries to flow, the diodes make sure it always exits the bridge in the same direction, turning it into DC. This makes the diode bridge a very effective full-wave rectifier.
Images for kids
-
A rectifier diode (silicon controlled rectifier) and its mounting hardware. The heavy threaded stud attaches the device to a heatsink to help it cool down.
-
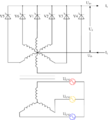
A circuit for a controlled three-phase half-wave rectifier, using thyristors as switches.
-
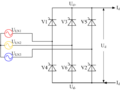
A circuit for a controlled three-phase full-wave rectifier, also using thyristors, with a special transformer.
-
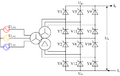
A controlled three-phase full-wave bridge rectifier circuit (B6C) using thyristors as switches.
-
A twelve-pulse bridge rectifier using thyristors as switches.
See also
 In Spanish: Rectificador para niños
In Spanish: Rectificador para niños
 | Misty Copeland |
 | Raven Wilkinson |
 | Debra Austin |
 | Aesha Ash |