Recuay culture facts for kids
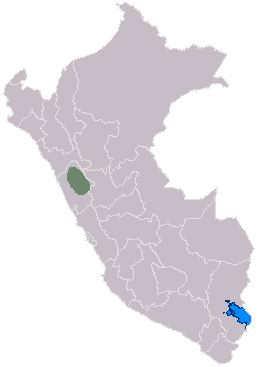
Map of the Recuay culture
|
|
| Geographical range | Callejón de Huaylas |
|---|---|
| Period | Early Intermediate |
| Dates | c. 200 BCE – 600 CE |
| Preceded by | Chavín culture |
| Followed by | Wari culture |

The Recuay culture was an ancient group of people who lived in the mountains of Peru. They were around from about 200 BCE to 600 CE. This means they lived a long time ago, even before the famous Inca Empire! The Recuay people were related to the Moche culture, who lived on the coast to the north. Their culture is named after the Recuay District in the Ancash Region of Peru.
Contents
Where the Recuay People Lived
The Recuay culture grew in a valley called the Callejón de Huaylas. Their special art style is sometimes called "Huaylas" because of this valley.
How They Were Influenced
The Recuay area was very close to where the older Chavín culture lived. The important Chavín site, Chavin de Huantar, was nearby. The Recuay people eventually lived in much of the Chavín's old territory. They learned a lot from the Chavín, especially about building with stone and making sculptures. For example, they used underground tunnels in their buildings, just like the Chavín did. Their pottery was also influenced by the Moche culture.
Other Cultures Nearby
While the people living on the coast of Peru, like the Moche, Lima, and Nasca cultures, are well-known, other strong groups also lived in the high mountains. These included the Cajamarca in the north, the Huarpa in the central mountains, and the Pucará near Lake Titicaca.
Living in a Strong Society
The Recuay people likely had a difficult relationship with the Moche culture to the north. They shared borders and needed the same water sources. There is proof that they often fought wars. Their buildings were strong and fortified, showing they were ready for battle. The Recuay are known for building some of the first fortified towns in the Peruvian Andes mountains.
The Recuay people built special rectangular tombs. These tombs had many rooms and different levels.
Where They Spread
The Recuay culture was strongest in the Callejón de Huaylas region. They also lived along the Marañón River. Their influence reached the valleys of the Santa, Casma, and Huarmey rivers. To the north, they reached an area called Pashash. Willkawayin was one of their important towns.
Recuay Pottery
Recuay culture is famous for its unique pottery. They used three main colors: black, red, and white. Recuay artists were very skilled. They sculpted small figures of people, jaguars, llamas, and other animals. Then, they attached these figures to their pots. Their pottery style is similar to the Virú culture's pottery. The Viru Valley is just north of the Recuay area.
Special Clay and Designs
Like the Cajamarca people, Recuay potters used a special white clay called kaolin. Working with this clay was very complex. After being heated in a kiln, the pottery turned a beautiful white color. A common animal in Recuay art is called the "moon animal." It looks like a fox or a cat with a long, toothy snout and a crest on its head.
Other Recuay Art
The Recuay people also made very high-quality textiles (fabrics). These textiles often had the same designs as their pottery.
They also carved stones, which are called Aija. These stone carvings are found all over the Peruvian Highlands. They are similar to the carvings made by the Pucará and Tiwanaku cultures.
Pashash Culture

The Pashash culture (500 – 1000 CE) is thought to be a later stage of the Recuay culture. It developed in the northern mountains of Ancash, in the Cabana region. You can find remains of this culture in towns like Chacas and Cabana, Peru.
During this time, metalworking was also very advanced. At Pashash, archaeologists found beautiful Recuay-style jewelry made of gilded bronze. They also found fine pottery from between 300 and 600 CE.
Images for kids
-
This pot looks like a palace or tomb. It was made by the Recuay people between 200 BCE and 600 CE. You can see it at the De Young Museum.
-
This is an engraved stone from Cabana, Peru. It belongs to the Pashash culture and is from around 500 CE.
See also
 In Spanish: Cultura recuay para niños
In Spanish: Cultura recuay para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |