SMRT Corporation facts for kids
 |
|
| Industry | Public transport |
|---|---|
| Founded | 6 August 1987 |
| Headquarters | 2 Tanjong Katong Road, #08-01, Paya Lebar Quarter (PLQ 3), Singapore 437161 |
|
Key people
|
Seah Moon Ming (chairman) Ngien Hoon Ping (from 1 August 2022) (group CEO) |
| Services | Bus & rail services |
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Owner | Temasek Holdings |
|
Number of employees
|
9,500 (March 2016) |
| Subsidiaries | SMRT Buses SMRT Trains Strides |
SMRT Corporation is a big company in Singapore that helps people get around. It runs buses and trains. SMRT is owned by Temasek Holdings, which is an investment company of the Government of Singapore.
The company started on 6 August 1987. For a while, its shares were traded on the Singapore Exchange. SMRT is one of the two main companies that operate Singapore's train services. The other one is SBS Transit.
Besides public transport, SMRT also rents out advertising space. It manages commercial areas inside the transport network. The company also offers services like maintenance and engineering advice. It even operates other transport services through its company called Strides.
Contents
History of SMRT
How Singapore's MRT Began
In 1967, city planners in Singapore thought a train system would be needed by 1992. Some important government ministers were against it at first. They worried about the high cost and if there would be enough jobs in construction.
One minister, Goh Keng Swee, suggested an all-bus system. He believed it would be much cheaper than building a train network. People had different opinions about this. Some were concerned about the cost, while others wanted better living standards.
After much discussion, Communications Minister Ong Teng Cheong decided that buses alone would not be enough. He knew that Singapore is a small country with limited road space. Mr. Ong was an architect and city planner. He worked very hard to make sure the train system was built.
Singapore's train system is built and managed by the government. The Land Transport Authority (LTA) builds the train lines and owns the equipment. This helps SMRT focus on running the trains smoothly.
The First Train Company
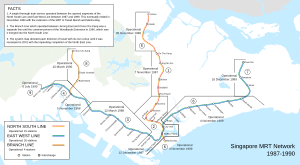
The Mass Rapid Transit Corporation (MRTC) was created on 14 October 1983. It took over from an earlier group that planned the MRT. The first chairman was Michael Fam. The first executive director was Lim Leong Geok.
On 7 November 1987, the MRTC started running Singapore's first MRT services. This first section had five stations. It ran from Yio Chu Kang to Toa Payoh.
On 1 September 1995, the MRTC joined with other government departments. They formed the Land Transport Authority (LTA). The job of running the MRT system was then given to SMRT Limited. This was a private company owned by the government's investment arm, Temasek Holdings.
SMRT Becomes a Public Company
In 1998, SMRT Limited took over ownership of the train system's equipment. This meant SMRT was responsible for maintaining the train lines and all their parts.
On 26 July 2000, SMRT Limited became a public company. It was listed on the Singapore Exchange as SMRT Corporation. Temasek Holdings sold some of its shares to the public.
In July 2001, SMRT bought another bus company called Trans-Island Bus Services (TIBS). This deal was completed in December 2001. TIBS became a company fully owned by SMRT. In May 2004, TIBS changed its name to SMRT Buses.
SMRT Returns to Government Control
In September 2016, Temasek Holdings bought all the remaining shares of SMRT. This meant SMRT was no longer traded on the Singapore Exchange. It returned to being fully owned by the government.
All of SMRT's train operating equipment was sold to the government. This happened under a new plan by the Land Transport Authority. SMRT's bus operating equipment was also sold to the government. This was part of the Bus Contracting Model.
Being "asset light" means SMRT does not own the expensive train and bus equipment. This allows SMRT to focus on making sure the public transport system runs reliably. It also helps SMRT work on business projects in other countries.
The High Court of Singapore approved the buy-out. The last day SMRT shares were traded was 18 October 2016. From 1 October 2016, the Land Transport Authority took over all the train operating assets from SMRT. This new plan helps SMRT focus on keeping the system reliable.
Recent Changes at SMRT
In 2023, SMRT Corporation combined its taxi services. Its Strides Taxi joined with Premier Taxis. They now operate together as Strides Premier.
SMRT's Services
SMRT's main job is to provide public transport in Singapore. As of 2015, it operates the following:
- SMRT Buses – SMRT has a fleet of up to 1,200 buses. These buses serve most housing areas in northern and north-western Singapore. They also cover the Jurong West Region.
- SMRT Trains – SMRT operates 119 stations on several MRT lines. These include the North–South, East–West, Circle, and Thomson–East Coast lines. SMRT also runs 13 stations on the Bukit Panjang LRT line.
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |