Serrate-leaved dryandra facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Serrate-leaved dryandra |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
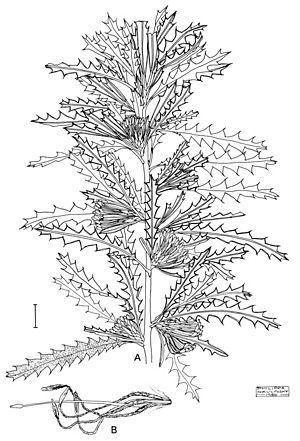
| An illustration of Banksia serra by Philippa Nikulinsky. | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Banksia |
| Subgenus: | Banksia subg. Banksia |
| Series: | Banksia ser. Dryandra |
| Species: |
B. serra
|
| Binomial name | |
| Banksia serra (R.Br.) A.R.Mast & K.R.Thiele
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Serrate-leaved Dryandra, also known as Banksia serra, is a special type of shrub. It grows only in Western Australia. This plant has long, saw-edged leaves. It also has pale yellow flowers that grow in groups of about thirty. After flowering, it produces egg-shaped seed pods called follicles.
Contents
What the Serrate-leaved Dryandra Looks Like
Banksia serra is a shrub that can grow up to 6 meters (about 20 feet) tall. It has thin stems. Unlike some plants, it does not have a special woody base called a lignotuber that helps it regrow after fires.
Its leaves are long and narrow, measuring 30 to 150 millimeters (about 1 to 6 inches) in length. They are 5 to 15 millimeters (about 0.2 to 0.6 inches) wide. The leaves grow on a short stalk called a petiole, which is 4 to 10 millimeters long. Each side of the leaves has 8 to 20 saw-like teeth.
The plant produces 20 to 36 pale yellow flowers. These flowers grow in groups, or "heads." At the base of each flower head are small, narrow, egg-shaped leaves called involucral bracts, which are 6 to 8 millimeters long.
Each flower has a part called a perianth, which is 16 to 19 millimeters long and mostly straight. The female part of the flower, called the pistil, is 19 to 21 millimeters long. It has a green tip called a pollen presenter. This plant flowers from July to October. Its seed pods, or follicles, are egg-shaped but curved, and they are 12 to 18 millimeters long.
How the Serrate-leaved Dryandra Got Its Name
This plant was first officially described in 1830 by a botanist named Robert Brown. He named it Dryandra serra. He published his description in a book called Supplementum primum Prodromi florae Novae Hollandiae. The plants he studied were collected by William Baxter near King George's Sound in 1829.
The second part of its name, serra, comes from a Latin word meaning "saw." This name was chosen because the leaves of the plant have saw-like edges.
Later, in 2007, two other scientists, Austin Mast and Kevin Thiele, moved all the plants in the Dryandra group into the Banksia group. That's why this plant is now called Banksia serra.
Where the Serrate-leaved Dryandra Lives
Banksia serra grows in the southwestern part of Western Australia. It can be found in different types of plant communities. These include woodlands, forests, and areas with mallee-kwongan vegetation. You can find it from the Bow River area all the way to Mount Manypeaks.
Serrate-leaved Dryandra and Its Environment
Scientists have studied how climate change might affect this plant. They found that the area where Banksia serra can grow might shrink a lot by the year 2080. Depending on how much the climate changes, its habitat could become 30% to 80% smaller.
Protecting the Serrate-leaved Dryandra
The Western Australian Government's Department of Parks and Wildlife keeps track of plant populations. They have classified Banksia serra as "not threatened." This means that, for now, there are enough of these plants in the wild that they are not considered to be in danger of disappearing.
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |


