Siege of Burriana facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Siege of Burriana |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Reconquista (Aragonese conquest of Valencia) | |||||||
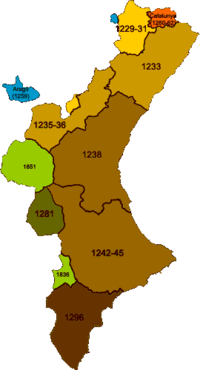 Chronological map documenting the Conquest of Valencia. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Taifa of Valencia | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Zayyan ibn Mardanish | |||||||
The Siege of Burriana was an important battle. It happened in 1233 during the Reconquista, a long period when Christian kingdoms in Spain took back land from Muslim rulers. King James I of Aragon led his army to capture the city of Burriana. Burriana was a key Muslim city, often called the "Green City." After two months of fighting, King James I's forces won in July 1233. This victory was a big step in his plan to conquer the Kingdom of Valencia.
Why the Siege Happened
In 1229, the city of Valencia was taken over by a local Muslim leader named Zayyan ibn Mardanish. He was against the ruling group, the Almohades. The previous ruler, Zayd Abu Zayd, had to leave Valencia and went to the Kingdom of Aragon.
King James I of Aragon saw this as a chance to expand his own kingdom. He decided to get involved in the Muslim civil war. He claimed he was helping the Almohades, but his real goal was to gain more land.
Two knights from Aragon, Hugo de Follalquer and Blas de Aragón, met with King James I. They had been in Valencia and told him how rich and successful the Muslim kingdom was. They encouraged the king to conquer it, which he decided to do in 1233.
What Happened Next
After King James I captured Burriana, other castles to the north also fell to his forces. These included important places like Peniscola, Castelló de la Plana, Borriol, les Coves de Vinromà, and Vilafamés.
Three years later, a very important battle took place. This was the Battle of the Puig in 1236. This battle was a major victory for King James I. It helped to secure the conquest of the entire Kingdom of Valencia.
See also
 In Spanish: Sitio de Burriana para niños
In Spanish: Sitio de Burriana para niños

