Solar sail facts for kids
A solar sail is a special way to move a spacecraft through space. It's also called a light sail or photon sail. Just like a boat uses wind to move, a solar sail uses the push from sunlight. This push is called radiation pressure.
The idea of using light to move things in space is quite old. A scientist named Johannes Kepler first thought about it in the 17th century. He imagined that "heavenly breezes" could push sails in space.
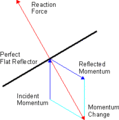
Later, in 1865, James Clerk Maxwell explained how light works. He showed that light, which is a type of electromagnetic radiation, can actually push on objects. This scientific discovery helped people understand how solar sails could work. When sunlight hits a solar sail, it reflects off it. This reflection creates a small push, or pressure.
Even regular spacecraft feel this push from the Sun. For example, a spacecraft traveling to Mars can be moved thousands of kilometers by solar pressure. Scientists always plan for this effect when designing spacecraft. Solar pressure also helps control which way a spacecraft is pointing.
The idea of solar sails has also appeared in science fiction stories, like those by Jules Verne.
How Solar Sails Work
The main idea behind a solar sail is to use the push from the Sun's light to move a spacecraft. Solar sails are usually very large, shiny surfaces, like huge mirrors.
One cool thing about solar sails is that they don't need propellant (fuel). As long as there is sunlight, they can keep moving. This makes them a good choice for future spacecraft missions. The push they get is very small, but it happens all the time. Over a long period, this small push can make a spacecraft go very fast.
For example, a solar sail that is 800 meters by 800 meters would get a push of about 5 newtons near Earth. This is a very gentle push, similar to what electric engines provide. But because it's constant, the spacecraft keeps speeding up.
The History of Solar Sails
Scientists have been planning to use solar sails for a long time. In the 1970s, two researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, Bruce Murray and Louis Friedman, worked on early plans.
The first successful use of a solar sail in space happened on May 21, 2010. Japan's Space Exploration Agency (JAXA) launched a solar sail called IKAROS. It traveled between Earth and Venus, proving that the idea worked.
In 2010, NASA also launched its first successful solar sail craft, called NANOSEL-D2.
More recently, on July 2, 2019, a group called The Planetary Society launched LightSail 2. This small satellite used solar sail technology. It was launched into space by a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Florida. This mission was special because it was funded by donations from many people. In late July 2019, LightSail 2 successfully opened its solar sail. This process took about three minutes.
Images for kids
-
IKAROS space-probe with solar sail in flight (artist's depiction) showing a typical square sail configuration
See also
 In Spanish: Vela solar para niños
In Spanish: Vela solar para niños