Sun tanning facts for kids
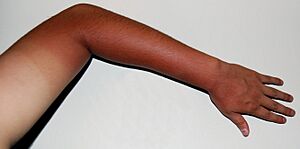
Sun tanning, or simply tanning, is when your skin gets darker. This usually happens when your skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays. These rays come from the sunlight or from special lamps in indoor tanning beds. Many people enjoy sunbathing to get a tan. You can also use special products to make your skin look darker without the sun, using products called sunless tanning lotions.
Contents
What is Sun Tanning?
Sun tanning is when your skin changes color and becomes darker. This happens because of special light rays called UV rays. These rays come from the sun or from tanning beds. People often sunbathe to get a tan. You can also use special products to make your skin look tanned without the sun.
How Does Skin Get Tanned?
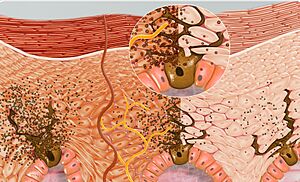
When your skin is exposed to UV rays, it produces a natural pigment called melanin. Melanin is what gives your skin, hair, and eyes their color. It also helps protect your skin from the sun's harmful rays.
Melanin: Your Skin's Natural Shield
Your skin has special cells called melanocytes. These cells make melanin. There are two main types of melanin: one that's reddish and one that's very dark brown. Melanin acts like a natural shield, absorbing UV radiation to protect your body.
When you get too much UV radiation, your body tries to fix the damage. It does this by making and releasing more melanin into your skin cells. This extra melanin makes your skin look darker, which we call a tan. This process can be started by natural sunlight or by artificial UV lamps.
UVA and UVB Rays: What's the Difference?
UV radiation is divided into different types, mainly UVA and UVB rays.
- UVA rays mostly cause existing melanin to darken quickly. This makes your skin look tanned right away. However, this type of tan doesn't offer much protection against sunburn.
- UVB rays are the main reason your body makes new melanin. This process takes a few days to become visible. The tan from UVB rays lasts longer and gives your skin some natural protection against future sun damage, like a small Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of about 3. UVB rays are also important for your body to produce Vitamin D.
Protecting Your Skin: Health and Safety
While a little sun can help your body make Vitamin D, too much UV exposure can be harmful.
The Dangers of Too Much Sun
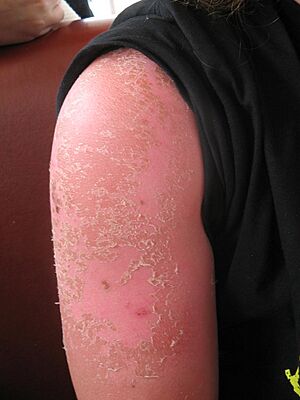
- Sunburn: Getting too much sun can quickly lead to painful sunburn. Some people burn more easily than others, depending on their skin color and genetics.
- Long-term Risks: Over time, too much sun can increase your risk of skin cancer. It can also make your skin age faster, causing wrinkles and spots. Too much UV can even affect your body's ability to fight off sickness.
- Tanning Beds: Using tanning beds frequently can significantly increase the risk of developing melanoma, a serious type of skin cancer. Health organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Cancer Society warn against excessive UV exposure from both the sun and tanning beds.
Smart Ways to Get a Tan (or Look Tanned)
To protect your skin, it's important to use sunscreen when you're outdoors. Sunscreen helps block UV rays and prevents sunburn. Even with sunscreen, it's best to limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during the strongest hours of the day.
Sunless Tanning Options
If you want to have darker skin without the risks of UV exposure, you can try sunless tanning products. These products, also called self-tanners, come as creams, lotions, gels, or sprays. They contain a special chemical that reacts with the top layer of your skin to create a temporary brown color. You can apply them yourself or get a professional spray tan at a salon. This way, you can get a tanned look safely.
How Does Your Skin React to the Sun?
Everyone's skin reacts differently to the sun. Your natural skin color plays a big role in how easily you tan or burn.
The Fitzpatrick Scale: Understanding Skin Types
In 1975, a doctor named Thomas B. Fitzpatrick created a scale to describe how different skin types react to the sun. It helps people understand their skin's natural tanning and burning tendencies:
| Type | Skin Color | Sunburning | Tanning Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Very light or pale | Often | Rarely tans |
| II | Light | Usually | Sometimes tans |
| III | Light intermediate | Rarely | Usually tans |
| IV | Dark intermediate | Rarely | Often tans |
| V | Dark | No | Darkens easily |
| VI | Very dark | No | Naturally dark brown |
Even if you have naturally dark skin, which offers some protection, it's still important to protect it from too much sun. Darker skin can still experience photoaging (skin aging from sun) and is at risk for melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
Why is Tanning Popular?
The idea of what makes skin look good has changed a lot over time!
A Look at Tanning Through History
Long ago, especially before the 1920s in Europe and the United States, having pale skin was seen as a sign of wealth. This was because people with money didn't have to work outdoors in the sun. They used parasols and wore long sleeves to keep their skin light.
However, things started to change in the 1920s. People began to see tanned skin as fashionable and healthy. This shift was partly influenced by famous people like fashion designer Coco Chanel. After she got a tan on a trip, her fans admired the look, and tanned skin became a trend.
Around the same time, scientists discovered that sunlight helped the body produce Vitamin D. This was important for preventing diseases like rickets. So, spending time in the sun became linked to good health.
Over the years, sunbathing became a popular activity. Advertisements encouraged it. Products like sun tan oils and later sunscreens became common. In the 1970s, even dolls like Malibu Barbie had tanned skin, showing how popular the look had become.
Today, while tanning is still popular, there's a greater understanding of the importance of sun protection.
See also
- Indoor tanning
- Skin whitening
- Sunburn
- Sunning