Indoor tanning facts for kids
Indoor tanning is when people use special machines that give off ultraviolet radiation (UV rays) to make their skin look darker, like a tan. You can usually find these machines in tanning salons, gyms, spas, hotels, and sometimes in homes. The most common type is a flat bed called a sunbed or solarium. There are also upright machines called tanning booths.
Indoor tanning became popular in the late 1970s, especially in places like Scandinavia. Most people who tan indoors are young women, usually between 16 and 25 years old. They often do it to feel better about how they look, to get a tan before a holiday, or sometimes to help with skin problems.
Even though many people use them, indoor tanning machines give off UV radiation, which is known to cause skin cancer, including a serious type called melanoma. It can also make your skin look older faster. Other risks include sunburn, eye damage like cataracts, and even infections. Doctors might use UV light to treat some skin conditions, like psoriasis, but health experts like the World Health Organization (WHO) do not recommend using tanning beds just for a cosmetic tan. The WHO even says that tanning devices are in the same group as things that definitely cause cancer, like UV rays from the sun.
Contents
What is Ultraviolet Radiation?
Ultraviolet radiation (UVR) is a type of energy that comes from the sun, and it's also what tanning machines use. You can't see it, but it's part of the electromagnetic spectrum, just beyond the light we can see.
UV light is split into three main types based on its wavelength (how long its waves are):
- UVA: These are the longest UV waves. About 95% of the UV light that reaches Earth from the sun is UVA. Tanning beds mostly use UVA.
- UVB: These waves are shorter than UVA. About 5% of the sun's UV light that reaches Earth is UVB. Tanning beds use a small amount of UVB.
- UVC: These are the shortest UV waves. Luckily, almost no UVC reaches Earth because our atmosphere blocks it. Modern tanning machines don't produce UVC.
UV radiation has both good and bad effects. While it can cause skin cancer and wrinkles, it also helps our skin make vitamin D, which is important for strong bones.
A Brief History of Tanning
For a long time in Europe and the United States, having very pale skin was a sign of being wealthy. People would use parasols and wear big hats to avoid the sun. But as more people started working in cities, pale skin became linked to poverty and poor health.
Then, in 1923, a famous fashion designer named Coco Chanel came back from a holiday with a tan, and it quickly became a fashion trend. Tanned skin was suddenly seen as stylish and a sign of good health.
Around the same time, doctors started talking about the benefits of "sun cures" for various health issues. This led to "sunlamps" being sold for home use in the 1920s. These early lamps gave off a lot of UVB, which often caused burns.
Later, a German scientist named Friedrich Wolff developed tanning beds that used mostly UVA and less UVB, which helped reduce burns. The very first tanning salon opened in Berlin in 1977. Soon after, tanning salons became popular across Europe and North America, and the indoor tanning industry began.
How Tanning Machines Work
Tanning Lamps
Tanning lamps, also called tanning bulbs, are what produce the UV light inside tanning machines. Most of these are long, low-pressure fluorescent tubes, similar to the lights you might see in a classroom, but they produce UV light instead of visible light.
Tanning Beds
Most tanning beds are horizontal (flat) machines with a bottom bench and a top lid. Inside, they have many long, low-pressure fluorescent bulbs under a clear surface. When you lie down and close the lid, you are surrounded by these bulbs.
Modern tanning beds mainly give off UVA rays. When you use a tanning bed, you set a timer, or a salon worker sets it for you. The maximum time for most low-pressure beds is about 15–20 minutes. This time is set by the manufacturer to limit how much UV radiation you get, to avoid burning your skin.
There are also "high-pressure" beds that use smaller, stronger bulbs. These beds give off even more UVA and have shorter maximum tanning times, usually 10–12 minutes. UVA rays give you an immediate tan by darkening the existing melanin in your skin. UVB rays don't give an immediate tan, but they make your skin produce new melanin, which leads to a longer-lasting tan. UVA is less likely to cause sunburn, but it can still cause wrinkles and make your skin lose its firmness because it goes deeper into the skin.
Tanning Booths
Tanning booths are vertical (stand-up) machines. You stand inside, holding onto handles, and are surrounded by tanning lamps. You usually close a door, but some designs are open. Booths often have more lamps than beds and usually have a maximum session time of 7–15 minutes. They work similarly to tanning beds, but some people prefer them for hygiene reasons, as you don't lie on a shared surface.
Lotions and Eye Protection
Before using a tanning machine, people often put on special indoor tanning lotion. These lotions don't contain sunscreen. Instead, they help moisturize the skin with ingredients like aloe vera and hempseed oil. Some lotions might also contain dihydroxyacetone, which is a sunless tanner that darkens the skin without UV light.
It's very important to wear special goggles (eye protection) when tanning indoors to protect your eyes from damage. Some people don't wear them to avoid getting pale circles around their eyes, but this is very risky. In many places, tanning salons are required to provide eye protection for their customers.
Who Uses Tanning Beds?
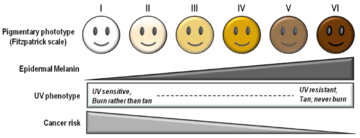
Indoor tanning is most popular among young white women, usually between 16 and 25 years old. These are often people who have lighter skin that doesn't burn too easily and who know other people who tan.
In the United States, the number of people using tanning beds has been going down. For example, between 2010 and 2013, the number of people aged 18–29 who tanned indoors fell from 11.3% to 8.6%. This might be partly because of a 10% "tanning tax" that was introduced in 2010.
Tanning bed use is also more common in northern countries, like Sweden, Denmark, and Germany. This might be because these areas have less natural sunlight for much of the year.
Why Do People Tan Indoors?
People choose to tan indoors for several reasons:
- Appearance: Many people believe that tanned skin makes them look healthier, more attractive, thinner, and more toned. They might also think it helps cover up skin blemishes like acne.
- Feeling Good: Some people say that tanning makes them feel relaxed and happy. This might be because UV exposure can increase levels of "beta-endorphins" in the body, which are linked to feelings of well-being.
- "Base Tan": Some people try to get a "base tan" before going on holiday, hoping it will prevent sunburn. However, studies show that indoor tanners still get sunburned. In fact, in some surveys, over half of indoor tanners reported getting burned during sessions.
- Skin Conditions: In some cases, doctors might recommend UV light therapy to treat certain skin conditions like psoriasis, eczema, or acne. Tanning beds in salons can sometimes be used for this if medical phototherapy isn't available.
Vitamin D Production
Our skin makes vitamin D when it's exposed to UVB light, whether from the sun or a tanning bed. Vitamin D is very important for strong bones and overall health. Some people use tanning beds specifically to get more vitamin D.
However, most health experts agree that the risks of skin cancer from tanning beds are much greater than the benefits of getting vitamin D this way. You can easily get enough vitamin D by taking supplements or eating foods that have vitamin D added to them.
Risks of Indoor Tanning
Using tanning beds comes with several serious risks, mainly because of the UV radiation they produce.
Skin Cancer Risk
Exposure to UV radiation, whether from the sun or tanning machines, is a major cause of skin cancer. There are two main types:
- Non-melanoma skin cancer: This includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. These are more common and usually not life-threatening if caught early.
- Melanoma: This is a less common but much more serious type of skin cancer. It causes most skin cancer-related deaths. Melanoma is the most common cancer in people aged 25–29 and the second most common in those aged 15–29. This might be partly because young people often have more UV exposure, including from indoor tanning.
Studies have shown that people who have used a tanning device at any point have a higher risk of melanoma. This risk increases even more for those who started using tanning beds before age 35.
Other Health Risks
UV radiation from tanning beds can also cause:
- Skin Aging: It can make your skin look older faster, leading to wrinkles, sunspots, and loss of skin firmness.
- Sunburn: Even though people try to avoid it, sunburns are common with indoor tanning.
- Eye Damage: UV rays can harm your eyes, leading to conditions like cataracts (cloudy vision) and even a rare type of eye cancer.
- Infections: Tanning beds can sometimes have germs on them that can cause skin infections or stomach problems if not cleaned properly.
- Photosensitivity: Some medicines, like certain antibiotics or antidepressants, can make your skin more sensitive to UV light, increasing your risk of severe burns from tanning.
Risks for Young People
Children and teenagers are at an even greater risk from UV radiation because their skin is more sensitive. Studies show that the more a young person uses artificial tanning, and the earlier they start, the higher their risk of developing serious skin cancer like melanoma.
Even if teenagers know about the risks, some studies show it doesn't always stop them from tanning. The tanning industry sometimes targets young people with ads and coupons. In 2012, a "sting" operation in the US found that many tanning salons didn't follow safety rules and gave misleading information about the risks and benefits to callers pretending to be 16-year-olds.
Rules About Indoor Tanning
Because of the health risks, many countries and regions have rules about indoor tanning.
- Australia: Commercial tanning services are banned in all states except one, where no salons operate anyway.
- Brazil: This country was the first to ban tanning beds for cosmetic use in 2009. They had already banned minors from using them in 2002.
- Canada: Many provinces in Canada ban indoor tanning for people under 18 or 19 years old.
- European Union: Several countries, including France, Austria, Germany, Ireland, and the United Kingdom, do not allow people under 18 to use tanning beds.
- United States: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says tanning beds are "moderate risk" devices. They require machines to have a warning that people under 18 should not use them, but they haven't banned it for minors nationwide. However, many US states and the District of Columbia have banned tanning for people under 18. Other states have strict rules, like needing parental permission for teenagers. In 2010, a 10% "tanning tax" was added to the cost of tanning services.
See also
 In Spanish: Solárium (centro de bronceado) para niños
In Spanish: Solárium (centro de bronceado) para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |