Three-sector hypothesis facts for kids
The Three-sector hypothesis is an idea in economics that helps us understand how countries develop. It says that there are three main types of jobs and activities in an economy, and they are very different from each other.
These types of activities are called economic sectors. The theory talks about the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors. This idea was first developed by thinkers like Alan Fisher, Colin Clark, and Jean Fourastié in the 1930s. It's also sometimes called Petty's Law because it builds on ideas from Sir William Petty from way back in 1690.
The theory also explains that as a country grows and becomes more developed, its main focus will shift. It usually moves from relying mostly on the primary sector to the secondary sector, and then from the secondary sector to the tertiary sector.
Contents
What Are the Three Sectors?
The Three-sector hypothesis divides all economic activities into three main groups. Let's look at each one.
Primary Sector: Getting Raw Materials
The primary sector is all about directly using natural resources. This means activities like:
- Farming (growing crops, raising animals)
- Fishing (catching fish)
- Forestry (cutting down trees for wood)
- Mining (digging for minerals like coal or gold)
Think of it as getting the basic ingredients from nature. In countries that are just starting to develop, a lot of people work in this sector.
Secondary Sector: Making Things
The secondary sector takes the raw materials from the primary sector and turns them into finished goods. This is often called manufacturing.
- Making cars from metal
- Building houses from wood and bricks
- Turning cotton into clothes
- Processing food from farms into packaged meals
This sector adds value to the raw materials by changing them into something more useful or complex. As countries develop, more people start working in factories and industries.
Tertiary Sector: Providing Services
The tertiary sector is all about providing services instead of making physical goods. This sector is also known as the service sector.
- Teachers helping students learn
- Doctors taking care of sick people
- Shop assistants selling products
- Hairdressers cutting hair
- People working in banks or tourism
In very developed countries, most people work in the tertiary sector. This shows how economies change over time, moving from basic activities to more complex services.
How Economies Change
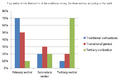
The Three-sector hypothesis suggests a path that most countries follow as they grow:
- Early Development: Most people work in the primary sector, getting raw materials.
- Middle Development: More people move into the secondary sector, making goods in factories.
- Advanced Development: The largest number of people work in the tertiary sector, providing services.
This shift shows how a country's economy becomes more advanced and diverse.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hipótesis de los tres sectores para niños
In Spanish: Hipótesis de los tres sectores para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |