Dental caries facts for kids
Dental caries, often called tooth decay or cavities, happens when tiny bacteria in your mouth damage your teeth. These bacteria create small holes in your teeth. If not treated, cavities can make your breath smell bad and give you a strange taste in your mouth. Taking good care of your teeth means brushing and flossing every day.
Your teeth have tough outer layers called enamel and dentin. If a cavity breaks through these layers, it can reach the soft inner part called the dental pulp. This pulp contains nerves. When these nerves are exposed, your tooth can become very sensitive. A bad cavity can even lead to an infection in your jaw, sometimes causing a painful abscess.
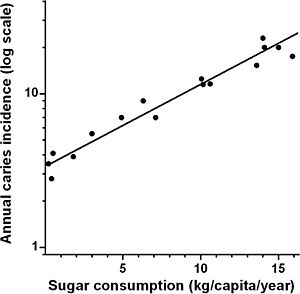
When you eat foods with carbohydrates (like sugars), bacteria in your mouth feed on them. They then form a sticky film called plaque on your teeth. This plaque attacks your tooth surface, leading to decay.
Contents
What Causes Cavities?
Cavities form when four main things come together. First, you need a tooth that can get a cavity. Second, you need certain bacteria in your mouth. Third, you need sugary foods or drinks. And fourth, these things need enough time to work.
When bacteria in plaque mix with sugars from your food, they create acids. These acids slowly dissolve the hard enamel of your teeth. Over time, this acid attack creates a hole, which is a cavity.
How Bacteria Attack Teeth
The main bacteria that cause cavities are called Streptococcus mutans. These tiny organisms love sugar. When you eat or drink sugary things, these bacteria eat the sugar too. As they digest the sugar, they produce acids.
These acids are strong enough to wear away the minerals that make up your tooth enamel. This process is called demineralization. If this continues, the enamel weakens and a cavity starts to form.
The Role of Plaque
Plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that constantly forms on your teeth. It feels fuzzy if you run your tongue over your teeth after a while. Plaque holds the acids close to your tooth surface, making it harder for your saliva to wash them away or neutralize them.
If plaque isn't removed by brushing and flossing, it can harden into something called tartar. Tartar is much tougher and can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist.
Sugary Foods and Drinks
Foods and drinks high in carbohydrates, especially sugars, are a major cause of cavities. This includes candy, soda, fruit juice, and even some starchy foods like chips or bread. The longer these sugars stay on your teeth, the more time bacteria have to produce acid.
Eating sugary snacks often throughout the day is worse than eating them all at once. This is because your teeth are exposed to acid attacks more frequently.
Signs and Symptoms
In the very early stages, you might not feel anything at all. As a cavity grows, you might start to notice some signs.
Tooth Sensitivity
One common sign is sensitivity. You might feel a sharp pain or discomfort when you eat or drink something hot, cold, or sweet. This happens when the cavity gets closer to the sensitive inner part of your tooth.
Visible Holes or Stains
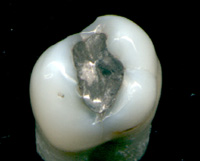
Sometimes, you can see a cavity as a small hole or pit in your tooth. It might look brown, black, or even white in some cases. You might also feel a rough spot with your tongue.
Pain When Chewing
If the cavity is more advanced, you might feel pain when you bite down or chew food. This can mean the decay has reached deeper into the tooth, possibly affecting the nerves.
Bad Breath or Taste
Cavities can trap food particles and bacteria, which can lead to bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
Preventing Cavities
The good news is that cavities are largely preventable! There are many simple steps you can take to keep your teeth healthy.
Brushing and Flossing
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste is very important. Make sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth. Flossing once a day helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under the gum line, where your toothbrush can't reach.

Healthy Eating Habits
Limit how often you eat sugary snacks and drinks. Try to choose healthier options like fruits, vegetables, and plain water. If you do have something sweet, try to eat it with a meal rather than as a separate snack. This is because saliva production increases during meals, which helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids.
Fluoride Protection
Fluoride is a natural mineral that helps make your tooth enamel stronger and more resistant to acid attacks. It can even help repair very early stages of decay. Fluoride is often added to tap water in many areas. It's also found in most toothpastes and some mouthwashes. Your dentist might also apply fluoride treatments to your teeth.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings is key. Your dentist can spot cavities early, sometimes even before you feel any symptoms. They can also give you professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar that you might miss at home.
Treating Cavities
If you do get a cavity, your dentist can usually fix it. The most common treatment is a dental filling.
Dental Fillings
To place a filling, the dentist first removes the decayed part of the tooth. Then, they clean the area and fill the hole with a special material. This material can be a tooth-colored composite resin, amalgam (a silver mixture), or other materials. The filling restores the tooth's shape and function.
Other Treatments
For very small cavities, sometimes fluoride treatments can help remineralize the tooth. For very large or deep cavities that have reached the pulp, a root canal might be needed. In some cases, if a tooth is too damaged to be saved, it might need to be removed.
Images for kids
-
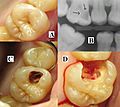
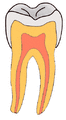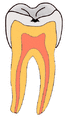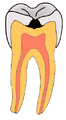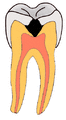
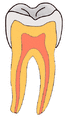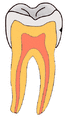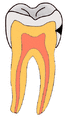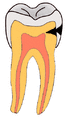
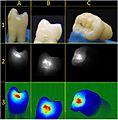
(A) A small spot of decay visible on the surface of a tooth. (B) The radiograph reveals an extensive region of demineralization within the dentin (arrows). (C) A hole is discovered on the side of the tooth at the beginning of decay removal. (D) All decay removed; ready for a filling.
See also
 In Spanish: Caries para niños
In Spanish: Caries para niños