Treaty of Nystad facts for kids
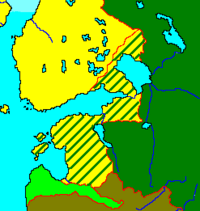
Treaty effects: pre-war Sweden in yellow, Russia in green, Russian gains indicated by lines.
|
|
| Signed | 10 September [O.S. 30 August] 1721 |
|---|---|
| Location | Nystad, Sweden (Present-day Uusikaupunki, Finland) |
| Original signatories |
|
The Treaty of Nystad was the final peace agreement that ended the Great Northern War. This big war lasted from 1700 to 1721. The treaty was signed between the Tsardom of Russia and the Swedish Empire.
It was signed on September 10, 1721. The signing took place in a town called Nystad. This town was part of Sweden back then. Today, it is known as Uusikaupunki in Finland. Sweden had already made peace with other countries. These agreements were signed in Stockholm and Frederiksborg.
Contents
War's Impact: Russia's Gains
During the Great Northern War, Peter the Great, who was the leader of Russia, took over many Swedish lands. These lands were located along the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea.
One important area he captured was Swedish Ingria. This is where he started building a new city in 1703. This city would later become St. Petersburg, the capital of Russia. Russia also took over Swedish Estonia and Swedish Livonia. These areas had surrendered to Russia in 1710. Russia also gained control of Finland during the war.
What the Treaty Changed
At Nystad, King Frederick I of Sweden officially agreed to give up several territories to Russia. These areas included Estonia, Livonia, Ingria, and parts of Southeast Finland. Specifically, Russia gained the Kexholm County and a section of the Karelian Isthmus.
In return for these lands, Russia paid Sweden two million silver thaler. A thaler was a type of silver coin. Russia also gave most of Finland back to Sweden.
Special Rights for Nobles
The treaty also included special rules for the German Baltic nobility in Estonia and Livonia. These were important families in those regions. The treaty allowed them to keep their financial system. They could also keep their existing customs borders.
They were allowed to govern themselves in many ways. They could also keep their Lutheran religion. The German language was also protected. Russian leaders, from Peter the Great to Alexander II of Russia, confirmed these special rights.
A New Balance of Power
The Treaty of Nystad showed a huge change in Europe. Before the war, Sweden was a very powerful empire. But after the war, its time as a major power ended. Sweden then entered a period called the Age of Liberty.
Meanwhile, Russia became a new and powerful empire. This treaty marked Russia's rise as a major force in Europe. It changed the way power was shared among European countries.
Legacy
In Saint Petersburg, before 1917, there was a street named after the Nystad treaty. It was called Nystadt Street. This street is now known as Lesnoy Prospekt. It was in the Vyborgsky district, which is close to the border with Finland.
In the same district, there is a church. It is called St. Sampsonius' Cathedral. This church remembers Russia's first big victory in the Great Northern War. That victory was the Battle of Poltava.
See also
- List of treaties




