Upland boneset facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Upland boneset |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Eupatorium sessilifolium drawing | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Eupatorium |
| Species: |
E. sessilifolium
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eupatorium sessilifolium |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Eupatorium sessilifolium, often called upland boneset or sessile-leaved boneset, is a plant found in North America. It belongs to the sunflower family. This plant grows naturally in the eastern and central parts of the United States. You can find it from Maine down to North Carolina and Alabama. It also grows west into states like Arkansas, Kansas, and Minnesota.
Contents
What Does Upland Boneset Look Like?
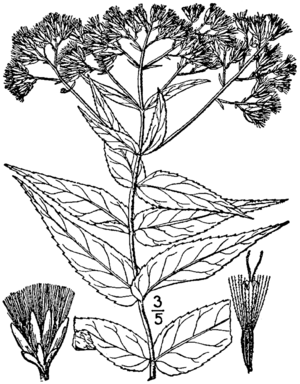
Upland boneset is a plant that lives for many years. It has stems that can grow taller than 100 centimeters (about 40 inches). These stems grow from a woody underground part called a caudex or a short rhizome. These are like special roots that help the plant spread.
Stems and Leaves
The upper parts of the stems, where the flowers grow, have short hairs. But the lower parts of the stems are smooth and have no hairs. The leaves grow in opposite pairs, meaning two leaves grow directly across from each other on the stem. The edges of the leaves are toothed, like tiny saw blades.
The bottom part of each leaf is rounded. The leaves are also "sessile," which means they attach directly to the stem without a small stalk. However, they do not wrap around the stem. The leaves also have tiny dots called glands.
Flowers and Blooming Time
Upland boneset usually blooms in August and September. If the plant is in the southern parts of its range, it might start blooming in July. Its small inflorescences (flower clusters) are branched. They have tiny white flower heads that are spaced out. These clusters form a flat-topped shape, which is called "corymbiform."
Each flower head typically has five or six small flowers called disc florets. These are the tiny flowers you see in the center of a sunflower. However, upland boneset does not have ray florets, which are the long petals that stick out from the edge of a sunflower.
Where Upland Boneset Lives
Upland boneset likes to grow in open woods or along the edges of wooded areas. It prefers soil that drains water well. Sometimes, you can also find it in small areas of old prairies, which are like natural grasslands.
Protecting Upland Boneset
This plant is considered a threatened species in Michigan. This means it is rare there and is legally protected by law. It is also a threatened species in Minnesota. In Minnesota, only a few groups of these plants exist, mostly in the very southeastern part of the state.
Plant Hybrids
Like many plants in the Eupatorium group, upland boneset can create "hybrids" with other species. A hybrid plant is a mix of two different parent plants.
For example, a plant called Eupatorium godfreyanum is a hybrid of E. sessilifolium and Eupatorium rotundifolium. Interestingly, Eupatorium godfreyanum can reproduce on its own without needing another plant to pollinate it. This special way of reproducing is called apomixis. Because of this, it can sometimes be found growing outside the areas where its two parent plants live.
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |


