Asteraceae facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Asteraceae |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: |
Asteraceae
Bercht. & J.Presl
|
| Genera | |
|
See text |
|

The Asteraceae family, also known as Compositae, is often called the aster, daisy, or sunflower family. It's the largest family of flowering plants on Earth, with the most different types of species.
What makes them special is their "flower heads." These aren't just one flower! They are actually made of hundreds or even thousands of tiny individual flowers packed closely together. This clever design is called a pseudanthium, which means "false flower." It looks like one big flower, but it's many small ones working together.
Contents
What are Asteraceae plants like?
Most plants in the Asteraceae family are herbaceous plants. This means they have soft, green stems, not woody ones like trees. However, some are shrubs, climbing plants, or even small trees.
It's usually easy to spot an Asteraceae plant because of its unique flower heads. But figuring out the exact type of plant within this family can sometimes be tricky!
Roots and stems
Most Asteraceae plants have a main root that grows straight down, called a taproot. Some have many thin roots that spread out. Their stems are usually green and branched. They often stand upright, but some can lie flat on the ground or grow upwards at an angle.
Some species have underground stems. These can be thick and fleshy or woody, depending on the plant.
Leaves
The leaves and stems of these plants often have special tubes that hold resin or a milky liquid called latex. You might see this if you break a dandelion stem.
The leaves can grow in different ways:
- They can be alternate, meaning they grow one after another on opposite sides of the stem.
- They can be opposite, growing in pairs across from each other.
- Or they can be whorled, forming a circle around the stem.
Their leaves can be simple, or they might have deep cuts or jagged edges. The edges of the leaves can be smooth, lobed, or toothed.
Amazing flowers
What looks like a single flower on an Asteraceae plant is actually a group of many tiny flowers. This cluster works like one big flower to attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies. The old family name, Compositae, comes from the word "composite," meaning it's made of many parts.
The "petals" you see on a sunflower are not true petals. They are actually individual, strap-shaped flowers called "ray flowers." The center part, the "sun disk," is made of many small, circular "disc flowers." The word "aster" means "star" in Greek, which describes how some of these star-like flowers look with their "rays."
The entire flower head can even move to follow the sun, just like a "smart" solar panel! This helps them reflect more light and attract more pollinators.
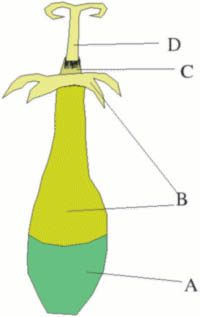
Parts of the flower head
At the bottom of the flower head, there are special leaf-like parts called phyllaries. These surround and protect the tiny individual flowers before they open. Together, these phyllaries form a protective cup called an involucre.
The small individual flowers, called florets, sit on a round or dome-shaped base called the receptacle. The florets on the outside of the head usually open first, and then the ones in the middle open later.
Each tiny floret has five petals that are joined together. Instead of typical sepals (the green parts that protect a bud), they have thread-like or bristly structures called a pappus. This pappus surrounds the fruit and helps the seeds spread. For example, the fluffy white head of a dandelion that children love to blow is made of pappus. It acts like a tiny parachute, helping the seeds float away on the wind.
Types of florets
- A ray flower is a strap-shaped floret, usually with three tips, found on the edge of the flower head. These are the "petals" of a daisy or sunflower.
- A ligulate flower is a strap-shaped floret with five tips. Some plants in this family only have ligulate flowers.
- A disc flower is a small, round floret found in the center of the flower head. These are the tiny flowers that make up the "sun disk" of a sunflower.
Different kinds of flower heads
- A radiate head has disc flowers in the middle surrounded by ray flowers on the outside. Sunflowers and daisies are good examples.
- A ligulate head has only ligulate flowers. Dandelions have this type of head.
- A discoid head has only disc flowers. These can be sterile, male, or have both male and female parts.
- Sometimes, very rarely, a flower head might have only one single flower!
Fruits and seeds
The fruit of an Asteraceae plant is called a cypsela. Even though it forms from two fused parts, it only contains one seed. The pappus (those bristly or hairy structures) often stays attached to the fruit. This helps the seeds travel, for example, by sticking to animal fur or being carried by the wind, like with a dandelion.
However, in some plants, like the sunflower, the pappus falls off. The shape and features of the cypsela are very important for scientists to identify different types of plants within this family. The mature seeds usually have very little or no endosperm (food storage tissue).
Images for kids
-
Senecio madagascariensis (Fireweed) is an environmental weed in Australia.
See also
 In Spanish: Asteráceas para niños
In Spanish: Asteráceas para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |