Variance facts for kids
The variance is a way to measure how much a group of numbers is spread out. Imagine you have a list of test scores. Variance tells you if the scores are all very close to each other or if they are very different.
It shows how much a number in a group tends to differ from the average of that group. Variance is found by taking the average of the squares of these differences. Because of this, variance is always a positive number.
You might see variance shown with symbols like 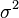 (sigma squared) if you're looking at a whole group of data. If you're only looking at a small part of the data, it's often shown as
(sigma squared) if you're looking at a whole group of data. If you're only looking at a small part of the data, it's often shown as 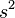 .
.
In simple terms, variance measures how much something changes. For example, the temperature in Moscow changes a lot more throughout the year than the temperature in Hawaii. This means Moscow's temperature has more variance.
Variance is not just the average difference from the expected value. The standard deviation, which is the square root of the variance, is closer to the average difference. Variance and standard deviation are used because they make mathematical calculations easier, especially when you are combining different groups of numbers.
What is Variance?
Variance helps us understand how spread out a set of numbers is. If the variance is small, the numbers are generally close to the average. If the variance is large, the numbers are more spread out from the average.
For example, if a group of students all score around 80% on a test, the variance of their scores would be small. If some students score 20% and others score 90%, the variance would be much larger.
Why Do We Use Variance?
Variance is a very important idea in statistics. It helps scientists, economists, and many others understand data better. For instance, a company might look at the variance in how long it takes to make a product. If the variance is high, it means the time changes a lot, which could point to problems in the production process.
It's also used in things like:
- Quality control: To make sure products are consistent.
- Finance: To measure the risk of investments.
- Science experiments: To see how much results vary.
History of Variance
The idea of variance was first used by a scientist named Karl Pearson. He was a very important person in the field of biometry, which uses statistics to study living things. In the late 1800s, he talked about how to measure how much things change in a group. He realized that the "standard deviation" (which is related to variance) was a good way to measure this.
Related Ideas
- Normal distribution: This is a common pattern that data follows, and variance is one of the key numbers used to describe it.
- Mean: This is the average of a set of numbers. Variance tells us how much numbers spread out from this average.
See also
 In Spanish: Varianza para niños
In Spanish: Varianza para niños

