White Salmon Glacier (Mount Adams) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids White Salmon Glacier |
|
|---|---|
| Type | Mountain glacier |
| Coordinates | 46°11′59″N 121°30′10″W / 46.19972°N 121.50278°W |
| Area | 0.51 km2 (0.20 sq mi) in 2006 |
| Length | .60 mi (0.97 km) |
| Terminus | Icefall |
| Status | Retreating |
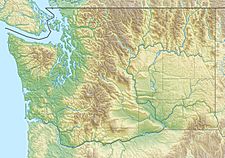
The White Salmon Glacier is a cool ice formation found on Mount Adams in the state of Washington, USA. This glacier is like a slow-moving river of ice. It starts high up on the mountain and flows downhill.
Contents
What is the White Salmon Glacier?
The White Salmon Glacier is a type of glacier that forms on mountains. It is located on the southwest side of Mount Adams. This mountain is a large stratovolcano in the Cascade Range. The glacier begins near the top of the mountain.
Where Does the Glacier Start and End?
The White Salmon Glacier starts southwest of the main summit crater. This is at a high elevation of about 11,600 ft (3,500 m). From there, the ice slowly moves downhill towards the southwest. The end of the glacier, called its terminus, is at about 9,600 ft (2,900 m) elevation.
How Does it Connect to Other Glaciers?
The White Salmon Glacier is not alone on Mount Adams. It actually shares some of its ice with another, much bigger glacier. This larger glacier is called the Avalanche Glacier. The White Salmon Glacier adds ice to the Avalanche Glacier at an elevation of about 10,200 ft (3,100 m).
Changes Over Time
Like many glaciers around the world, the White Salmon Glacier has been getting smaller. This process is called glacial retreat. It means the glacier is melting faster than new snow and ice can build up.
How Much Has it Shrunk?
Scientists have been watching the White Salmon Glacier for many years. They found that its surface area has shrunk a lot. Between the years 1904 and 2006, the glacier lost 86 percent of its size. This is a very big change in just over a hundred years.
Why Do Glaciers Shrink?
Glaciers shrink for different reasons. One main reason is a warming climate. When temperatures get warmer, ice melts more quickly. Less snow also falls in some areas, which means less new ice forms to replace what melts. Studying glaciers like White Salmon helps scientists understand how our planet is changing.
 | Misty Copeland |
 | Raven Wilkinson |
 | Debra Austin |
 | Aesha Ash |