Williamson River (Oregon) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Williamson River |
|
|---|---|

The Williamson River near Chiloquin
|
|
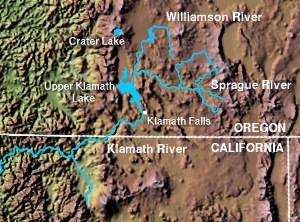
The Williamson, Sprague, and Klamath rivers
|
|
|
Where the Williamson River meets Upper Klamath Lake
|
|
| Country | United States |
| State | Oregon |
| County | Klamath |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | near Bottle Spring Winema National Forest 5,100 ft (1,600 m) 42°42′15″N 121°20′24″W / 42.70417°N 121.34000°W |
| River mouth | Upper Klamath Lake near Modoc Point 4,147 ft (1,264 m) 42°27′53″N 121°57′25″W / 42.46472°N 121.95694°W |
| Length | 100 mi (160 km) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 3,000 sq mi (7,800 km2) |
The Williamson River is a river in south-central Oregon, United States. It is about 100 miles (160 km) (160 km) long. The river helps drain an area of about 3,000 square miles (7,800 km2) (7,800 km²) east of the Cascade Range.
The Williamson River and its main branch, the Sprague River, provide more than half the water flowing into Upper Klamath Lake. This lake is the largest freshwater lake in Oregon. From Upper Klamath Lake, the water flows into the Link River. The Link River then connects to Lake Ewauna and finally the Klamath River.
Contents
Where Does the Williamson River Start?
The Williamson River begins from a large spring in central Klamath County. This spring is on the north side of Fuego Mountain. It is located in the Winema National Forest, about 40 miles (64 km) (64 km) northeast of Klamath Falls.
How the River Flows
The river first flows north through the mountains. Then it turns west and later southwest. It passes through Klamath Marsh and the Klamath Marsh National Wildlife Refuge.
Further downstream, the river flows next to U.S. Route 97. It receives water from Spring Creek on its right side. This is near Collier Memorial State Park, about 5 miles (8.0 km) (8 km) north of Chiloquin.
At Chiloquin, the Sprague River joins the Williamson River from the left side. The Williamson River then flows into the northern part of Upper Klamath Lake. This meeting point is near Modoc Point, about 20 miles (32 km) (32 km) northwest of Klamath Falls.
What is the Williamson River Watershed?
A watershed is an area of land where all the water drains into a single river or lake. The Williamson River watershed covers a large area.
Land Use in the Watershed
In the lower parts of the watershed, near the big streams, there are farms. These farms use water from the river to grow crops and feed for animals. Many areas in the basin are used for livestock grazing.
Forests cover about 81% of the watershed. These forests are often used for timber. Farms make up about 6% of the land. The remaining 13% includes range lands, wetlands, water bodies, and urban areas.
Rainfall in the Area
The basin is in the rain shadow of the Cascade Range. This means it gets less rain. The average rainfall is about 23 inches (580 mm) (580 mm) per year along the Williamson River before it meets the Sprague River. Along the Sprague River, the average is about 20 inches (510 mm) (510 mm) per year.
Fun Things to Do: Recreation on the River
The Williamson River is famous for its large wild Great Basin redband trout. These fish are a type of rainbow trout. They swim into the river to lay their eggs and to escape the warm waters of Upper Klamath Lake. Three-year-old fish often grow to 20 inches (51 cm) (50 cm) or more.
Smaller numbers of brown trout also live in the Williamson River. They are especially found below Spring Creek. Lost River suckers also live in the river. However, these fish are protected, so you cannot catch and keep them. Smaller rainbow trout and brook trout live in the river above Klamath Marsh.
Much of the land along the river is owned by private individuals. This means that public access to the river for fishing or other activities can be limited.
History of the Williamson River Area
Since 2003, groups like The Nature Conservancy have been working to restore the Williamson River delta. This area is about 12 square miles (31 km2) (31 km²) of wetlands at the north end of Upper Klamath Lake.
Restoring the Delta
In the past, this delta area was drained and used for farming. Now, efforts are being made to bring back the wetlands. This helps create a home for millions of migrating birds. It also provides habitat for many native fish, mollusks, and water plants.
Ancient Times
Long ago, during the early Pleistocene period, Klamath Marsh and Upper Klamath Lake were much bigger. They stayed as shallow lakes and marshes because the land slowly sank. At the same time, new land was pushed up along the eastern fault line.
About 7,700 years ago, the Mt. Mazama volcano erupted. This eruption added a huge amount of dirt and rock to the lake and marsh basins. It also filled the canyon of the Williamson River.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Río Williamson (Oregón) para niños
In Spanish: Río Williamson (Oregón) para niños