Upper Klamath Lake facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Upper Klamath Lake |
|
|---|---|

Aerial view of Williamson River and Agency Lake
|
|
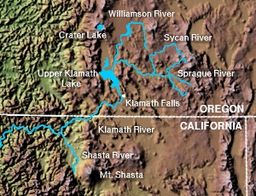
Upper Kalamath Lake Watershed
|
|
| Location | Klamath County, Oregon, United States |
| Coordinates | 42°23′32″N 121°52′49″W / 42.39222°N 121.88028°W |
| Lake type | Hypereutrophic |
| Primary inflows | Williamson River, Wood River, Crooked Creek, Fourmile Creek |
| Primary outflows | Link River |
| Catchment area | 3,768 sq mi (9,760 km2) |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 20 mi (32 km) |
| Max. width | 8 mi (13 km) |
| Surface area | 61,543 acres (24,906 ha) |
| Average depth | 14 ft (4.3 m) |
| Water volume | 849,290 acre⋅ft (1.04758 km3) |
| Residence time | 0.5 months |
| Shore length1 | 87.8 mi (141.3 km) |
| Surface elevation | 4,140 feet (1,260 m) |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Upper Klamath Lake is a large, shallow freshwater lake in south-central Oregon, United States. It is the biggest freshwater body in Oregon by surface area. The lake stretches about 25 miles (40 km) long and 8 miles (13 km) wide. It extends northwest from the city of Klamath Falls. The lake sits at an average height of 4,140 feet (1,260 m) above sea level.
In the early 1900s, many wet areas around the lake were drained for farming. This damaged the natural homes for animals and plants. The lake's water has been used for about 100 years to help farmers with irrigation through the federal Klamath Project. The lake's depth changes because its water supply is controlled. It usually ranges from 8 to 50 feet (2.4 to 15.2 m) deep. The water level is kept at a certain height to protect fish in the lake and coho salmon in the Klamath River below.
Upper Klamath Lake gets its water from a large area of 3,768 square miles (9,760 km2). This includes the Williamson and Wood Rivers. The lake drains into the Klamath River, which starts at the south end of the lake as the Link River. A short channel connects Upper Klamath Lake to the smaller Agency Lake to the north. The Upper Klamath National Wildlife Refuge is located along the northern edge of the lake. It helps protect the natural environment there.
Contents
What is the History of Upper Klamath Lake?
How Was Upper Klamath Lake Formed?
Upper Klamath Lake is the largest part left of a huge ancient lake called Lake Modoc. This giant lake existed in the area about 10,000 years ago. At its biggest, Lake Modoc covered over 1,000 square miles (2,600 km2). It connected Upper Klamath, Lower Klamath, and Tule Lakes. It also included all the major wetlands in the upper Klamath River basin. This ancient lake was more than ten times the size of today's Upper Klamath Lake. It was also nearly 100 feet (30 m) higher in elevation. Lake Modoc disappeared as the climate became warmer and drier at the end of the Pleistocene Ice Age.
Who Lived Around Upper Klamath Lake?
The area around Upper Klamath Lake and the Williamson, Sprague, and Wood Rivers was originally home to the Klamath people. The Modoc people lived south of Upper Klamath Lake, near the Lower Klamath and Tule lakes.
The first people of European descent to visit Upper Klamath Lake were fur trappers in December 1826. They were led by Peter Skene Ogden from the Hudson's Bay Company. Ogden called the lake "Dog Lake" because he traded for dogs from the local Klamaths for food. They explored the lake and the Klamath River with help from native guides.
Conflicts and Changes Around the Lake

As more settlers came to the region, there were conflicts between American immigrants and Native Americans. In 1846, a military group led by John C. Frémont and Kit Carson was attacked near Upper Klamath Lake. In response, Frémont and Carson's group attacked a local village, and fourteen people died.
The Modoc people resisted the settlers by raiding parties along the South Emigrant Trail. This trail went through the Klamath River Valley south of Upper Klamath Lake. In 1873, the Native Americans were defeated in the Modoc War. They were then moved to a reservation on the north side of the lake.
The lake has always been known for its water quality. Frémont noted the "often foul smelling waters" of the lake. The Applegate Trail was even planned to avoid the lake. This was because the water was "so bad that it might be too dangerous for livestock to drink late in the season."
Starting in the mid-1800s, the valleys north and south of Upper Klamath Lake were settled for farming. Since 1917, the water level in the lake has been controlled. This is done by the United States Bureau of Reclamation (BOR)'s Link River Dam. It is part of the Klamath Reclamation Project. This project provides water for farming in the upper Klamath Basin. The original dam was made of timber. It was replaced by a stronger concrete dam in 1921.
What is the Ecology of Upper Klamath Lake?
How Have Wetlands Changed Around the Lake?
Before the 1900s, the lake was surrounded by many marshes and wetlands. These areas were home to fish, birds, and other wildlife. They also helped keep the lake water clean. However, much of these important natural areas were drained. They were turned into farmland because farmers did not understand how valuable wetlands were for the environment.
Why Does the Lake Have Algae Blooms?
The lake naturally has a lot of nutrients, which means it is eutrophic. In the 1900s, more nutrients came into the lake from farm runoff. This made the lake hypereutrophic, meaning it has too many nutrients. This causes large blooms of blue-green algae (mostly Aphanizomenon flos-aquae). These algae blooms turn the water a thick green color in the summer. They also make it harder to use the lake for fun activities like boating. The amount of dissolved oxygen in the water often falls below state standards. This puts fish in danger.
What Wildlife Lives in Upper Klamath Lake?
Despite the water quality issues, the lake is still a very important stop for waterfowl along the Pacific Flyway. It is also known for its rainbow trout fishing.
The US Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) works to protect and maintain the sucker fish populations in the lake. In 1988, the FWS put the Lost River sucker and the shortnose sucker (Catostomidae) on the federal endangered species list. The numbers of these two fish species, which used to be very common in Upper Klamath Lake, had dropped sharply. This was due to the decline in water quality. Because of this, the government stopped a planned project to make a deeper channel in the lake. This project would have further harmed the water quality.
What Are the Challenges for Upper Klamath Lake?
A drought in the summer of 2001 made environmental concerns about the lake even bigger. The BOR stopped taking irrigation water from the lake for the Klamath Project. This was done to protect the sucker fish population. The farming community protested because they relied on the lake's water for their farms. As of 2003, the FWS was regularly checking the lake. This was because water shortages put both the fish in the lake and the salmon in the Klamath River at risk. The future uses of Klamath Lake are important to many people. There are different ideas about how to use the lake, including farmers' property rights and larger environmental goals.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lago Upper Klamath para niños
In Spanish: Lago Upper Klamath para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |