Wolbachia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Wolbachia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
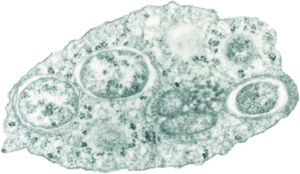
| A tiny Wolbachia bacterium inside an insect cell, seen with a special microscope | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: |
Alphaproteobacteria
|
| Order: |
Rickettsiales
|
| Family: |
Rickettsiaceae
|
| Genus: |
Wolbachia
|
Wolbachia is a special type of bacteria that lives inside many different kinds of arthropods. Arthropods are creatures with exoskeletons, like insects, spiders, and crustaceans. This tiny bacterium is one of the most common parasites in the world. It often affects how insects reproduce, making it a very important part of the natural world.
Contents
What is Wolbachia?
Wolbachia is a very small living thing, so tiny you can only see it with a powerful microscope. It lives inside the cells of its host, which is usually an insect. Think of it like a tiny passenger living inside a bigger animal.
These bacteria are very common. Scientists believe that more than half of all insect species on Earth might have Wolbachia living inside them! This makes Wolbachia one of the most widespread bacteria in the world.
How Wolbachia Spreads
Wolbachia has a clever way of spreading. It usually passes from a mother insect to her babies. This happens when the mother lays eggs, and the bacteria are already inside the eggs. So, when the babies hatch, they already have Wolbachia too!
This way of spreading means that Wolbachia mostly affects the female insects and their offspring. It's like a family secret passed down through generations.
Wolbachia's Superpowers
Wolbachia is known for its amazing abilities to change how insects reproduce. It can do several surprising things to its insect hosts. These changes help the bacteria spread even more.
Changing Insect Reproduction
Wolbachia can influence insects in different ways. Sometimes, it makes it harder for infected males and uninfected females to have babies together. This is called cytoplasmic incompatibility. It means that if a male with Wolbachia mates with a female without it, their eggs might not hatch. But if both parents have Wolbachia, or if an uninfected male mates with an infected female, they can have healthy babies. This encourages the spread of Wolbachia in the insect population.
In some cases, Wolbachia can even change the sex of an insect. For example, it might turn male insects into females. This is called feminization. In other cases, it might cause female insects to produce only female offspring, or even to reproduce without a male at all. This is called parthenogenesis. These "superpowers" help Wolbachia make sure there are more females carrying the bacteria, which helps it spread to more babies.
Helping Fight Diseases
Even though Wolbachia is a parasite, it can also be very helpful to humans! Scientists are using Wolbachia to fight diseases like dengue fever, Zika virus, and chikungunya. These diseases are spread by mosquitoes.
Here's how it works: When mosquitoes are infected with certain types of Wolbachia, the bacteria can make it much harder for the mosquitoes to carry and spread viruses like dengue. So, if we release mosquitoes with Wolbachia into areas where these diseases are common, they can mate with wild mosquitoes. Over time, more and more mosquitoes in that area will have Wolbachia. This helps to reduce the spread of dangerous diseases to people. It's a natural way to protect communities from mosquito-borne illnesses.
This method is a safe and environmentally friendly way to control diseases. It doesn't use harmful chemicals and works with nature to solve a big problem.
Images for kids
-
Adi Utarini, a lead researcher for the Wolbachia project in Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
See also
 In Spanish: Wolbachia para niños
In Spanish: Wolbachia para niños



