Younger Dryas facts for kids
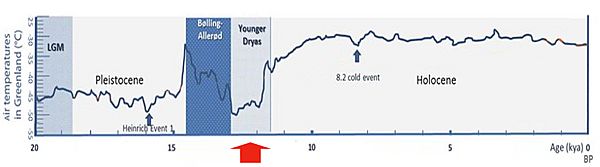
The Younger Dryas was a very cold time. It happened about 12,900 to 11,700 years ago. This cold snap stopped the Earth from slowly getting warmer. That warming had started around 20,000 years ago.
During the Younger Dryas, temperatures dropped sharply. This happened across most of the Northern Hemisphere. It took place at the very end of the Pleistocene epoch. This was just before our current, warmer time, called the Holocene epoch.
Contents
What Was the Younger Dryas?
The Younger Dryas was the most recent cold period. It was also the longest. It interrupted the Earth's slow warming after the last big ice age. That ice age is known as the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). The LGM happened about 27,000 to 24,000 years ago.
How Cold Did It Get?
The temperature change during the Younger Dryas was quite sudden. In Greenland, temperatures dropped a lot. They fell by 4 to 10 degrees Celsius (7.2 to 18 degrees Fahrenheit). This made glaciers grow bigger. It also caused dry conditions in many parts of the Northern Hemisphere.
What Caused This Big Change?
Scientists think a large amount of cold, fresh water flowed into the Atlantic Ocean. This water came from North America. This sudden rush of cold water might have changed ocean currents. This then led to the big drop in temperatures.
How Did It Affect Different Places?
The Younger Dryas caused different effects around the world. In some places, like the Southern Hemisphere, it actually got a little warmer. Some areas in the Northern Hemisphere, such as southeastern North America, also saw a slight warming. So, the changes were not the same everywhere.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Dryas Reciente para niños
In Spanish: Dryas Reciente para niños