Active transport facts for kids
Active transport is a special way that tiny parts, called molecules, move into and out of cells. Imagine a cell as a house with a fence around it. Active transport is like bringing groceries into the house even when there are already a lot of groceries inside. It means moving molecules from a place where there are fewer of them to a place where there are more.
This kind of movement needs energy. Cells often get this energy from a special molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Cells use active transport to get important things they need, like ions (tiny charged particles), glucose (sugar for energy), and amino acids (building blocks for proteins).
Normally, molecules like to spread out from a crowded area to a less crowded area. Think of a drop of food coloring spreading in water. But with active transport, cells do the opposite! They pull molecules into the cell even when there are already many molecules inside. This is called moving against the concentration gradient.
To do this hard work, cells use special helpers called proteins. These proteins act like tiny doors or pumps in the cell's outer layer, the cell membrane. Molecules cannot just float through the cell membrane on their own. They need these protein "doors" to get in or out.
How Cells Move Things In
Cells use different kinds of protein doors to move molecules. These doors are very specific about what they let through and how they use energy.
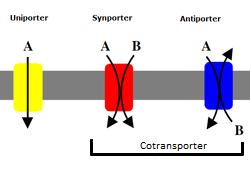
Types of Protein Doors
There are three main types of protein doors in cell membranes:
- Uniporters: These proteins use energy from ATP to pull just one type of molecule into the cell. It's like a single-person elevator for molecules.
- Symporters: These proteins are clever! They let one molecule move into the cell, and as that molecule moves, it helps pull a second molecule in at the same time, even if the second molecule is moving against its concentration gradient.
- Antiporters: These proteins are like a revolving door. They let one substance move out of the cell while using that movement to pull another substance into the cell. They often use the energy from common ions like sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), or hydrogen (H+).
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Transporte activo para niños
In Spanish: Transporte activo para niños