Acute radiation syndrome facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Acute radiation syndrome |
|
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Radiation poisoning, radiation sickness, radiation toxicity |
 |
|
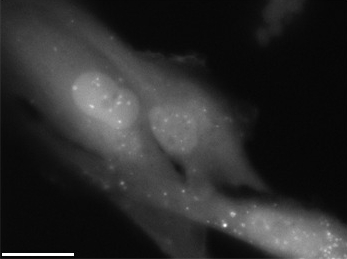
| Radiation causes cellular degradation by autophagy. | |
| Symptoms | Early: Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite Later: Infections, bleeding, dehydration, confusion |
| Usual onset | Within days |
| Types | Bone marrow syndrome, gastrointestinal syndrome, neurovascular syndrome |
| Causes | Large amounts of ionizing radiation over a short period of time |
| Diagnostic method | Based on history of exposure and symptoms |
| Treatment | Supportive care (blood transfusions, antibiotics, colony stimulating factors, stem cell transplant) |
| Prognosis | Depends on the exposure dose |
| Frequency | Rare |
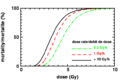
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS), often called radiation sickness or radiation poisoning, is a group of health problems that happen when someone is exposed to a lot of ionizing radiation very quickly. This radiation usually comes from outside the body. It happens quickly, often in minutes, and affects most of the body.
At first, symptoms might include feeling sick to your stomach (nausea), throwing up (vomiting), and not wanting to eat. Then, for a few hours or even weeks, you might feel better with few symptoms. After this quiet period, depending on how much radiation someone got, they might get infections, bleeding, feel very thirsty (dehydration), or become confused. These symptoms can start within an hour and might last for several months. Eventually, they either get better or sadly, they don't survive.
Contents
What is Acute Radiation Syndrome?
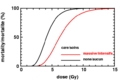
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) happens when a person's body is exposed to a very high amount of ionizing radiation in a short time. This type of radiation has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms, which can damage cells and DNA in the body. The amount of radiation needed to cause ARS is usually more than 0.7 Gy.
Types of Radiation Sickness
ARS is usually divided into three main types, depending on which body systems are most affected:
- Bone marrow syndrome: This is the most common type. It affects the bone marrow, which makes blood cells. When bone marrow is damaged, the body can't make enough new blood cells, leading to problems like infections and bleeding.
- Gastrointestinal syndrome: This type affects the stomach and intestines. It can cause severe nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, leading to dehydration and problems absorbing nutrients.
- Neurovascular syndrome: This is the most severe type and happens with very high doses of radiation. It affects the brain and blood vessels, causing confusion, seizures, and a rapid decline in health.
How Does Radiation Cause ARS?
The cells most harmed by radiation are usually those that divide and grow very quickly. These include cells in your bone marrow (which makes blood), the lining of your stomach and intestines, and your hair follicles. When these cells are damaged, they can't do their jobs properly, leading to the symptoms of ARS.
Sources of this strong radiation can include nuclear power plants, cyclotrons (machines that speed up tiny particles), and special equipment used in cancer treatment.
Diagnosing and Treating ARS
Doctors diagnose ARS by looking at a person's history of exposure to radiation and their symptoms. They also use repeated complete blood counts (CBCs), which are blood tests that count different types of blood cells. These tests can help show how severe the radiation exposure was.
Treatment for ARS mainly focuses on supportive care. This means helping the body heal and managing the symptoms. Treatments might include:
- Blood transfusions: To replace damaged blood cells.
- Antibiotics: To fight infections, as the body's immune system is weakened.
- Colony-stimulating factors: Medicines that help the bone marrow make more blood cells.
- Stem cell transplant: In very severe cases, healthy stem cells can be given to help the bone marrow recover.
If radioactive material is still on the skin or in the stomach, it needs to be removed quickly. If a specific type of radioactive material called radioiodine was breathed in or swallowed, a medicine called potassium iodide might be given. This helps protect the thyroid gland.
People who survive ARS might have a higher risk of developing other health problems later, like leukemia and other cancers. These are managed like any other cancer. How well someone recovers depends a lot on how much radiation they were exposed to.
Notable Cases
Acute radiation syndrome is generally rare. However, a single event can affect many people. Famous examples include the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 and the Chernobyl disaster at a nuclear power plant in 1986.
It's important to know that ARS is different from chronic radiation syndrome. Chronic radiation syndrome happens when someone is exposed to small amounts of radiation over a very long time, not a large amount quickly.
Images for kids
-
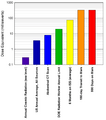
Comparison of Radiation Doses – includes the amount detected on the trip from Earth to Mars by the RAD on the MSL (2011–2013).
See also
 In Spanish: Síndrome de irradiación aguda para niños
In Spanish: Síndrome de irradiación aguda para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |