Mars Science Laboratory facts for kids
| Mars Science Laboratory mission | |
|---|---|
 2011 concept artwork |
|
| Organization: | NASA |
| Major contractors: | Boeing Lockheed Martin |
| Mission type: | Rover |
| Launch date: | November 26, 2011 (10:02 am, Eastern Time Zone) |
| Launch vehicle: | Atlas V 541 (AV-028) |
| Launch site: | Cape Canaveral LC-41 |
| Mission duration: | 668 Martian sols (686 Earth days) |
| NSSDC ID: | MARSCILAB |
| Webpage: | Mars Science Laboratory |
| Mass: | 900 kg (2,000 lb) |
| Power: | Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator |
| Planet: | Mars |
| Landing: | August 6, 2012 |
Quick facts for kids edit |
|
The Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a special NASA mission. Its main goal was to send a robot called Curiosity to the planet Mars. The MSL spacecraft launched on November 26, 2011.
Curiosity made a very accurate landing on Mars. It landed in a place called Gale Crater on August 5, 2012. Right after landing, it started exploring the Martian surface.
The Mission's Big Goal
The main reason for the Curiosity rover mission is to learn about Mars's past. Scientists wanted to know if Mars ever had an environment where tiny living things, called microbes, could have survived.
Curiosity found exciting clues! It discovered evidence that about 3 billion years ago, Mars had water. It also had an environment that could have supported life. It's important to remember that Curiosity found that life could have existed, not that it definitely did. The rover also carefully studies samples of soil and drilled rock powders.
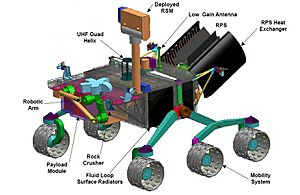
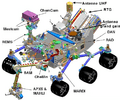
Meet the Curiosity Rover
Curiosity is much bigger and heavier than earlier Mars rovers like Spirit or Opportunity. It weighs five times more! It also carries more than ten times the amount of science tools.
The rover was launched into space by a powerful Atlas V 541 rocket. Curiosity was designed to work for at least one Martian year. That's 668 Martian sols, or 686 Earth days. However, it has already worked much longer than that! It can explore Mars over a wider area than any other rover before it.
Who is Behind the Mission?
The Mars Science Laboratory mission is part of NASA's bigger Mars Exploration Program. This program is a long-term plan to send robotic spacecraft to explore Mars. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) manages this program for NASA. JPL is part of the California Institute of Technology. The whole MSL project cost about US$2.3 billion.
Images for kids
-
Hubble view of Mars: Gale crater can be seen. Slightly left and south of center, it is a small dark spot with dust trailing southward from it.
-
Diagram of the MSL spacecraft: 1- Cruise stage; 2- Backshell; 3- Descent stage; 4- Curiosity rover; 5- Heat shield; 6- Parachute
-
Goldstone antenna can receive signals
-
Wheels of a working sibling to Curiosity. The Morse code pattern (for "JPL") is represented by small (dot) and large (dash) holes in three horizontal lines on the wheels. The code on each line is read from right to left.
-
The RAD on Curiosity.
-
MSL's cruise stage being tested at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory near Pasadena, California
-
Aeolis Mons rises from the middle of Gale Crater – Green dot marks the Curiosity rover landing site in Aeolis Palus – North is down
-
NASA's Curiosity rover and its parachute were spotted by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter as the probe descended to the surface. August 6, 2012.