Bonefish facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bonefish |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: |
Albuliformes
|
| Family: |
Albulidae
|
| Genus: |
Albula
|
| Species: |
A. vulpes
|
| Binomial name | |
| Albula vulpes (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Species
Esox vulpes Linnaeus 1758
Vulpis vulpes (Linnaeus 1758) ?Albula lacustris Walbaum 1792 Albula conoryncha Bloch & Schneider 1801 Clupea brasiliensis Bloch & Schneider 1801 non Steindachner 1879 Albula plumieri Bloch & Schneider 1801 Amia immaculata Bloch & Schneider 1801 Clupea macrocephala Lacépède 1803 Conorynchus macrocephalus (Lacépède 1803) ?Butyrinus bananus Lacepède 1803 Glossodus forskalii Spix & Agassiz 1829 Engraulis bahiensis Spix 1829 Engraulis serica Spix 1829 Albula parrae Valenciennes 1847 Albula goreensis Valenciennes 1847 Esunculus costai Kaup 1856 Vulpis bahamensis Catesby 1771 Albulas gronovii Walbaum 1792 Albula rostrata Gronow 1854 ?Albula unbarana Marcgrave ex de Castelnau 1855 |
|
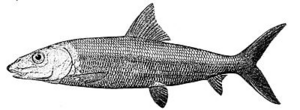
The bonefish (Albula vulpes) is a type of fish known for living in shallow, warm ocean waters. It belongs to the bonefish family, called Albulidae. This family is the only one in its larger group, the Albuliformes.
Contents
Discovering the Bonefish Species
For a long time, people thought there was only one type of bonefish found all over the world. But scientists have now discovered that there are actually nine different species!
Where Bonefish Live
Three of these bonefish species live in the Atlantic Ocean. The other six species are found in the Pacific Ocean. The Albula vulpes is the biggest and most common bonefish species in the Atlantic.
What Bonefish Look Like
Bonefish can grow quite large. They can weigh up to 14 pounds (about 6.4 kg) and be as long as 79 centimeters (about 31 inches). Their bodies are usually silver on the sides. Their backs can be a bit darker, sometimes olive green.
Bonefish Colors and Markings
You might see soft, subtle lines running along their sides from their gills to their tail. These lines come from slight shading on their scales. The bases of their pectoral fins (the fins on their sides) are sometimes yellow.
Bonefish Life Cycle
Bonefish can live for up to 20 years. They become old enough to have babies when they are about 2 to 3 years old. At this age, they are usually longer than 17 inches (about 43 cm). Baby bonefish, called larvae, float in the ocean for about 53 days. Young bonefish often live in areas with open sandy bottoms.
How Bonefish Behave
Bonefish are a type of fish that moves between fresh and saltwater, though they mostly stay in the ocean. They live in warm, coastal waters. When the tide comes in, they move onto shallow mudflats or sand flats to find food.
Bonefish Social Life
Both adult and young bonefish sometimes swim together in groups called shoals. Older adult bonefish might also be seen swimming alone or in pairs.
What Bonefish Eat
Bonefish mostly eat small creatures that live on the ocean floor. These include worms, small fish, crabs, shrimp, and shellfish. They find lots of these small prey near ledges, drop-offs, and healthy seagrass beds.
Sometimes, bonefish will even follow stingrays. They do this to catch the small animals that the stingrays dig up from the sand or mud. In one specific area, the Los Roques archipelago, bonefish mostly hunt tiny fish called glass minnows. However, this is not typical behavior for bonefish in other places.
Fishing for Bonefish
Bonefish are very popular for sport fishing, especially with fly and light fishing tackle. Fishing for bonefish, often called "bonefishing," is a popular sport in places like the Bahamas, Puerto Rico, and southern Florida.
How to Catch Bonefish
Since bonefish live in shallow water near the coast, people can fish for them by wading in the water. They can also fish from special boats that don't need deep water. Most bonefishing is done for fun, so fishermen usually release the fish back into the water.
Bonefish as Food
In some less developed areas, bonefish are eaten. A common recipe in the Bahamas is to split the fish, season it with pepper sauce and salt, and then bake it.
Bonefish are known for being very careful and easily scared. Fishermen need to be very skilled when approaching them and casting their lines. Because they are so hard to catch, English-speaking fishermen often call them "grey ghosts."
See also
 In Spanish: Macabijo para niños
In Spanish: Macabijo para niños




