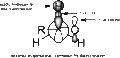Aldol reaction facts for kids
The aldol reaction is a super important reaction in organic chemistry. Think of it as a special way to build bigger molecules from smaller ones. It was first discovered way back in 1872!
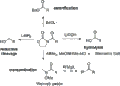
This reaction is like a molecular building game. It takes two special types of molecules called carbonyl compounds. With a little help from a base (which is a chemical that can accept a proton), these two smaller molecules can join together. They form a new connection between their carbon atoms. This creates a larger, more complex molecule.
One cool thing about the aldol reaction is that it can help create molecules with specific 3D shapes. This is called stereochemistry. It's like building with LEGOs, but making sure each piece is in the exact right spot to create a perfect model. This ability to control the shape is very useful for making new types of molecules, especially in medicine.
How the Aldol Reaction Works
Imagine you have two small building blocks. The aldol reaction helps them connect. One of the blocks has a special carbon atom next to its C-O double bond. A base helps this carbon atom become "sticky." It then reaches out and connects to the carbon atom of the other building block.
This joining creates a new, larger molecule. This new molecule has a C-O double bond and an alcohol group (a carbon with an -OH group) two carbon atoms away. It's a powerful way to combine simple ingredients into something much more complex.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Reacción aldólica para niños
In Spanish: Reacción aldólica para niños