Apollo Lunar Module facts for kids
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM) was a special spacecraft. It looked a bit like a giant spider! Its job was to carry two astronauts from orbit around the Moon down to its surface. After exploring, it would then take them back up to meet the main spacecraft.
This amazing vehicle was part of the US Apollo program. It was designed to help humans land on the Moon for the very first time. NASA decided to build the LM after choosing a plan where a smaller craft would land on the Moon, while the main spacecraft stayed in orbit.
The Lunar Module was tested many times in space. Finally, on July 20, 1969, the Apollo 11 LM, named Eagle, made history. It successfully landed the first humans on the Moon!
After this, other Apollo missions like Apollo 12, 14, 15, 16, and 17 also used their LMs to land on the Moon. The Lunar Module even played a heroic role during the Apollo 13 mission. When an oxygen tank exploded, the Apollo 13 LM, called Aquarius, became a safe haven. It helped save the lives of the three astronauts, bringing them safely back to Earth.
Contents
What Was the Lunar Module Like?
The Lunar Module was made of two main parts. These were the descent stage and the ascent stage.
The Descent Stage: Landing on the Moon
The descent stage was the lower part of the LM. It was shaped like an octagon and had four legs for landing. This part held important things like batteries, oxygen tanks, and scientific tools. These supplies were used during the trip down to the Moon and while the astronauts were exploring.
When landing, the descent engine would fire. This slowed the LM down as it dropped from orbit towards the Moon. The LM could even hover above the surface before a gentle touchdown. After the astronauts finished their Moonwalks, the descent stage stayed behind. It became the launchpad for the upper part of the LM to blast off from the Moon.
The Ascent Stage: Leaving the Moon
The ascent stage was the upper, rounder part of the LM. This was like the command center and the astronauts' cabin. It also had the rocket that would launch them away from the Moon.
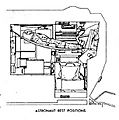
To save weight, there were no seats inside. The astronauts stood up, held loosely by straps. In front of them were control panels. These panels helped them guide the LM, talk to Earth, and control the air inside. The commander had a window on the left side to see where they were going.
Above them was a hatch, about 33 inches wide. This was where astronauts moved between the LM and the main Command Module when they were connected. The ascent rocket was small, but it was powerful enough. The Moon's gravity is much weaker than Earth's. This meant the LM didn't need a huge push to leave the lunar surface.
First Test Flight of the Lunar Module
The first test flight of a Lunar Module happened on January 22, 1968. This was part of the Apollo 5 mission. A 16-ton unmanned LM, protected by a shield, was launched on top of a Saturn 1-B rocket.
This test had two main goals. One was to check if the LM could separate from the main rocket. The other was to test fire its descent engine. The second part of the mission didn't go perfectly. The Apollo 5 test lasted for eight hours. The LM stayed in Earth orbit for a while before falling back into the atmosphere and burning up.
Images for kids
-
Lunar Module Eagle, the lunar module ascent stage of Apollo 11, in orbit above the Moon. Earth is visible in the distance. Photograph by Michael Collins.
-
The Apollo 6 Lunar Module Test Article (LTA-2R) shortly before being mated with the SLA
-
Decreased clearance led to buckling of the extended descent engine nozzle on the landing of Apollo 15
See also
 In Spanish: Módulo lunar para niños
In Spanish: Módulo lunar para niños