Argument of periapsis facts for kids
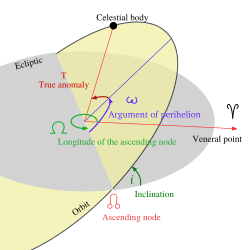
In astronomy, the argument of periapsis (ω) is a special way to describe the orbit of a planet, asteroid, or comet. It helps scientists understand exactly where an object is in its journey around another object. You might also hear it called the argument of perihelion (for objects orbiting the Sun) or argument of perifocus.
Contents
What is the Argument of Periapsis?
The argument of periapsis is an angle in an object's orbit. This angle tells us the position of the object's closest point to what it's orbiting. It's measured from a special starting line in space.
Understanding Periapsis
The term "periapsis" means the point in an orbit where an object is closest to the body it is orbiting.
- For example, when the Moon is closest to Earth, it is at its "perigee" (a type of periapsis).
- When a planet is closest to the Sun, it is at its "perihelion."
- "Pericenter" is a general term for the closest point in any orbit.
What is the Ascending Node?
The "ascending node" is another important point in an orbit. Imagine an imaginary flat surface called the "reference plane." This plane usually goes through the center of the object being orbited. The ascending node is one of two places where an orbiting object crosses this reference plane while moving from south to north.
How the Angle is Measured
The argument of periapsis angle is measured within the orbital plane. This is the flat surface where the orbiting object actually moves. The angle is measured in the same direction that the object is moving.
- If the argument of periapsis is 0°, it means the orbiting object reaches its closest point to the central body exactly when it crosses the reference plane from south to north.
- If the argument of periapsis is 90°, the orbiting object reaches its closest point when it is at its farthest north from the reference plane.
Argument of Perihelion and Longitude of Ascending Node for Planets
The table below shows the argument of periapsis (ω) and the longitude of ascending node (Ω) for the planets in our Solar System. These values help scientists track the exact paths of planets.
| Planet | Argument of periapsis (ω) in degrees | Longitude of Ascending node (Ω) in degrees |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 29.022 | 48.378 |
| Venus | 54.780 | 76.785 |
| Earth | 85.901 | 18.272 |
| Mars | 286.231 | 49.667 |
| Jupiter | 273.442 | 100.398 |
| Saturn | 336.178 | 113.759 |
| Uranus | 98.862 | 73.967 |
| Neptune | 256.932 | 131.823 |
| Pluto | 113.175 | 110.088 |
See also
 In Spanish: Argumento del periastro para niños
In Spanish: Argumento del periastro para niños
 | Anna J. Cooper |
 | Mary McLeod Bethune |
 | Lillie Mae Bradford |