Askia Mohammad I facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Askia Muhammad |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ruler of the Songhai Empire | |||||
| Reign | April 1493 – 1528 | ||||
| Predecessor | Sunni Baru | ||||
| Successor | Askia Monzo Mūsā | ||||
| Born | 1443 | ||||
| Died | 1538 Gao, Songhai Empire |
||||
| Burial | Tomb of Askia, Gao, Mali | ||||
| Issue | Ismail and Haibe | ||||
|
|||||
| Dynasty | Askia Dynasty | ||||
| Father | Arlum Sylla | ||||
| Mother | Kassaï | ||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||
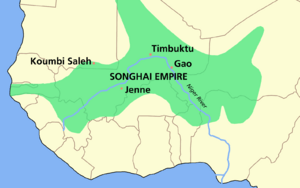
Askia Muhammad I (born Muhammad Ture Sylla in 1443) was a powerful leader of the Songhai Empire in West Africa. He is also known as Askia the Great. He was an emperor, a skilled military leader, and a political reformer. Askia Muhammad helped make the Songhai Empire the largest empire in West Africa's history.
Under his rule, the Songhai Empire grew very big. It included areas like the Hausa states and reached as far as Kano in modern-day Nigeria. His leadership led to more trade with Europe and Asia. He also created many schools and made Islam an important part of the empire.
After the previous ruler, Sunni Ali Ber, passed away, his son Sunni Baru was supposed to take over. However, Muhammad Ture, who was one of Sunni Ali Ber's generals, challenged him. Muhammad Ture believed Sunni Baru was not a faithful Muslim. General Ture won the fight and became the new ruler in 1493.
Askia Muhammad's Rule
General Ture, who later became known as Askia Muhammad I, worked to expand and strengthen the empire. He made the empire stretch from Taghaza in the North to Yatenga in the South. It also reached from Air in the Northeast to Futa Djallon in Guinea.
Askia Muhammad improved the way the empire was run. He set up a system of government with different departments. This was a very advanced system for West Africa at the time. He also created standard ways to measure goods for trade. He made rules for trading and kept trade routes safe. Plus, he set up an organized system for collecting taxes. In 1528, his own son, Askia Musa, took over the throne from him.
A Lasting Legacy
Askia Muhammad strongly encouraged learning and reading. He made sure that the universities in Songhai produced excellent scholars. Many of these scholars wrote important books. One famous scholar was his nephew and friend, Mahmud Kati.
To make his rule stronger, Askia Muhammad worked closely with the scholars of Timbuktu. This led to a "golden age" for the city. It became a center for scientific and Muslim learning. For example, the famous scholar Ahmed Baba wrote books on Islamic law that are still used today.
Two important history books were also written during this time. Muhammad Kati published Tarikh al-fattash. Abdul-Rahman as-Sadi wrote Tarikh al-Sudan, which means Chronicle of The Black Land. These books are very helpful for people today who study African history from the Middle Ages.
The place believed to be Askia Muhammad's tomb, called the Tomb of Askia, is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site. This means it's a special place recognized for its importance to the world.
See also
 In Spanish: Askia Mohamed I el Grande para niños
In Spanish: Askia Mohamed I el Grande para niños