Aspergillus fumigatus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Aspergillus fumigatus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: |
A. fumigatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius 1863
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Neosartorya fumigata |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Aspergillus fumigatus is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is very common in nature and plays an important role in the environment. It helps break down dead plants and leaves, which recycles nutrients like carbon and nitrogen back into the soil.
While this fungus is helpful in nature, it can sometimes cause health problems. It is one of the most common causes of fungal infections in people with a weak immune system.
Contents
Habitat and Characteristics
Aspergillus fumigatus is a saprotroph, which means it feeds on decaying organic matter. It is often found in soil and compost heaps.
This fungus is very tough. It can grow at normal human body temperature (37 °C or 99 °F) and can survive in much hotter places, up to 50 °C or 122 °F. Its spores can even survive at 70 °C or 158 °F. These warm conditions are common in compost piles that heat up as plants break down.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
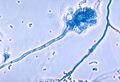
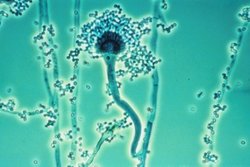
The fungus grows colonies that produce thousands of tiny grey-green spores called conidia. These spores are very small (2–3 μm) and float easily in the air.
For over 100 years, scientists thought A. fumigatus only reproduced by making copies of itself (asexually). However, in 2008, researchers discovered that it has a fully working sexual reproductive cycle. This ability helps the fungus maintain its population, even though it does not change much genetically across the world.
Interaction with Humans
The spores of A. fumigatus are everywhere in the air. Most people breathe in several hundred spores every day. In healthy people, the immune system quickly removes these spores without any trouble.
However, for people with weakened immune systems, the fungus can be dangerous. This includes people who have had organ transplants or have certain illnesses. In these cases, the fungus can grow inside the body and cause a group of diseases called aspergillosis.
How the Fungus Causes Illness
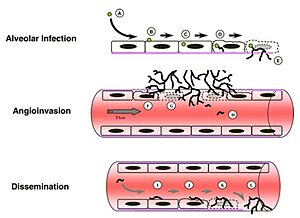
When a person with a weak immune system breathes in the spores, the spores may not be destroyed. Instead, they can wake up from their dormant state in the warm, moist environment of the lungs.
The spores grow into long thread-like structures called hyphae. These hyphae can grow into the lung tissue and sometimes enter the blood vessels. This process can damage cells and block blood flow.
Useful and Harmful Compounds
The fungus produces various chemical compounds. Some of these, called alkaloids, have been studied by scientists. One compound, spirotryprostatin B, is being researched as a potential medicine to fight cancer.
On the other hand, the fungus can also produce harmful toxins called mycotoxins. One example is gliotoxin, which can weaken the body's defenses.
Survival and Growth
To survive inside a host or in nature, A. fumigatus needs to find food. It has special genes that help it get nutrients like metals and nitrogen.
Getting Iron
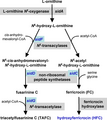
Iron is very important for the fungus to grow. It acts as a helper for many of the fungus's internal tools (enzymes). A. fumigatus has two main ways to get iron:
- It can change iron into a form it can absorb easily.
- It uses special molecules called siderophores to grab iron.
Studies show that using siderophores is essential for the fungus to cause infection. If the genes for making siderophores are removed, the fungus becomes less dangerous.
Getting Nitrogen
The fungus can use many different sources of nitrogen. The ability to absorb nitrogen is important for its growth. Scientists found that certain genes help regulate this process. When the fungus touches human cells, it turns on specific genes to help it get the nitrogen it needs.
Medical Treatments
Doctors use medicines called antifungals to treat infections caused by A. fumigatus. The most common type of medicine is known as azoles. Examples include voriconazole and itraconazole.
These drugs work by stopping the fungus from making ergosterol, which is a key part of its cell wall. Without it, the fungus cannot survive.
Recently, some strains of the fungus have become resistant to these medicines. This might be happening because similar chemicals are used in farming. Scientists are also looking at other types of medicines, like echinocandins, to help patients.
Virus in the Fungus
A. fumigatus can carry a virus called AfuPmV-1M. A study from 2025 found that this virus appears to make the fungus stronger. When infected mice were given antiviral drugs to target the virus, their chances of survival improved. This suggests that treating the virus might help fight the fungal infection.
Genome
The genetic code (genome) of A. fumigatus is about 29.4 million base pairs long. In December 2005, scientists published the complete genome sequence in the journal Nature. This helps researchers understand how the fungus works and how to treat infections.
Images for kids
See also
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Aspergilloma
- Fumagillin
- Galactosaminogalactan
- List of diseases of the honeybee
- New England Compounding Center meningitis outbreak (2012)
- RodA
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |