Atheris barbouri facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Atheris barbouri |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Subfamily: | Viperinae |
| Genus: | Atheris |
| Species: |
A. barbouri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Atheris barbouri Loveridge, 1930
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
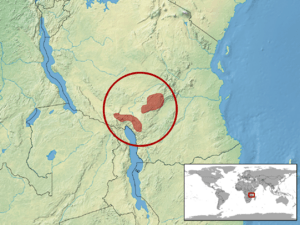
The Atheris barbouri is a small and rare type of viper. It lives only on land and is found only in the Uzungwe and Ukinga mountains. These mountains are located in south-central Tanzania, a country in Africa.
Contents
About the Uzungwe Mountain Bush Viper
Naming This Special Snake
The specific name, barbouri, was chosen to honor an American snake expert named Thomas Barbour. This snake has a few common names. People also call it the Uzungwe viper, Barbour's viper, or the Uzungwe mountain bush viper. Sometimes it's even called the worm-eating viper. Scientists do not recognize any subspecies for this snake.
When it was first discovered in 1930, Atheris barbouri was placed in the Atheris group, which are often called bush vipers. Later, in 1978, some scientists thought it was different enough to be put in its own group called Adenorhinos. This was because it looked a bit different from other Atheris snakes.
However, newer research in 2001 suggested it was actually closely related to another Atheris species, Atheris ceratophora. So, in 2011, it was moved back into the Atheris group. Scientists are still studying it. They want to be sure if it should stay in Atheris or if it needs its own special group.
Similar Snakes
Atheris barbouri is similar to two other snakes: Montatheris hindii and Proatheris superciliaris. These snakes also live on land. They were once thought to be part of the Atheris group too.
What Does It Look Like?
Size and Shape
The Atheris barbouri is a small snake. It only grows to about 40 centimeters (16 inches) long, including its tail. Its head is wide and shaped like a triangle. It stands out from its neck. The snout, which is the front part of its head, is short and rounded.
Its eyes are quite big and noticeable. They are about 1.5 times larger than the distance to its mouth. The nostril is very far forward on its nose. It is part of a single scale that touches the scale in front of its eye.
Scales and Skin
The snake's body is fairly thin. Its tail is shorter than the tails of other Atheris snakes. It cannot use its tail to grab onto things like some other snakes can.
Its back scales are arranged in 20 to 23 rows around the middle of its body. Most of these scales have a strong ridge, which makes them feel rough. However, the scales on the very edges of its body are smooth. The scales on its belly are rounded and number between 116 and 122. The scales under its tail are single, not divided, and there are 19 to 23 of them. The scale covering its vent (where waste leaves the body) is also a single scale.
Colors and Patterns
The Atheris barbouri usually has a brown or blackish-brown body color. It has two zigzag stripes that run along its back, one on each side. These stripes start behind its head and go all the way to the end of its tail. Sometimes, these stripes look like a chain of darker, diamond-shaped spots down its back. Its tail might have a faint, dark checkered pattern. The snake's belly is usually greenish-white or olive green.
Where Does This Viper Live?
Its Home in Tanzania
The A. barbouri's home is very small. It is only found in the Uzungwe and Ukinga mountains. These mountains are in the south-central part of Tanzania, Africa.
The first place this snake was officially found was in "Dabaga, Uzungwe Mountains." This area is southeast of Iringa, Tanzania, at an altitude of about 1,800 meters (6,000 feet).
Preferred Places to Live
This snake lives on land. It is often found in bushes and thick bamboo plants on mountain slopes. It seems to prefer moist forest areas. However, it has also been seen in gardens on tea farms.
How Does It Live?
Not much is known about how the A. barbouri behaves. At first, some thought it might be a snake that burrows underground. But it doesn't have any special body features that would help it dig. So, it probably doesn't burrow much.
What Does It Eat?
Scientists believe that A. barbouri mostly eats soft-bodied creatures. This includes slugs, earthworms, and other small, squishy animals. It might also eat frogs.
Baby Vipers
The Atheris barbouri is thought to lay eggs. This means it is an oviparous species. In February 1930, three female snakes were found. Each of them had 10 eggs inside. The largest egg was about 1.0 by 0.6 centimeters (0.4 by 0.2 inches) in size.
About Its Venom
There is not much information about the venom of A. barbouri. We don't know what its venom is made of or how strong it is. No one has ever reported being bitten by this snake. Because it lives in such a small area, it is very unlikely that people will encounter it and get bitten.
Images for kids