Bismarck (ship) facts for kids
The German battleship Bismarck was one of the most famous warships of World War II. It was built by Nazi Germany. The Bismarck only sailed for one big mission, known as Operation "Rheinübung". Its construction started on July 1, 1936, in Hamburg, Germany. It was launched into the water on February 14, 1940. The Bismarck was one of the largest battleships ever built by a European country. It was the biggest built by Nazi Germany, along with its sister ship, the Tirpitz.
About the Bismarck
The Bismarck and Tirpitz were planned in the mid-1930s. The German navy, called the Kriegsmarine, wanted them to be strong enough to challenge France's growing navy. Construction began in 1936. These ships were supposed to stay under a weight limit of 35,000 long tons. This limit was set by international agreements like the Washington regime and the Anglo-German Naval Agreement.
However, Germany secretly ignored these limits. Before the Bismarck was even finished, these agreements broke down. This happened because Japan left the treaties in 1937. The Bismarck actually weighed 41,700 tons when empty. When it was fully loaded, it weighed 50,300 tons (49,500 long tons). It was 251 meters (823 feet 6 inches) long. This made it the largest battleship built by any European country until the HMS Vanguard was built after the war.
The Bismarck could travel very fast. It reached a top speed of 30.01 knots (about 55.58 km/h or 34.53 mph) during its tests. It could travel a maximum distance of 16,430 km (10,210 miles) without needing to refuel. The ship had a large crew of 2,000 to 2,200 people. They were divided into twelve groups. Half of the crew worked with the main and secondary guns. The other half were support staff, like cooks and radio operators.
The Bismarck had many powerful weapons. It had eight large 38 cm (15 inch) guns. It also had twelve 15 cm (5.9 inch) guns, sixteen 10.5 cm (4.1 inch) guns, sixteen 3.7 cm (1.5 inch) guns, and twelve 2 cm (0.79 inch) guns. The ship was also heavily armored. Its main armor belt was 320 mm (12.6 inches) thick. It also had upper and main armor decks that were 50 mm to 120 mm (2 inches to 4.7 inches) thick. The front of its gun turrets were protected by 360 mm (14.2 inches) of armor, and the sides were 220 mm (8.7 inches) thick.
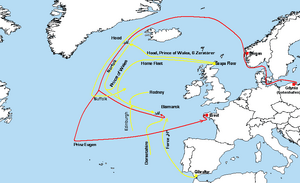
Operation "Rheinübung"
On May 5, 1941, Adolf Hitler started Operation Rheinübung. The goal was to cut off Britain's vital supply lines. These lines were made up of merchant ships bringing important goods like food and raw materials to Britain. If these supplies were stopped, Britain might have been forced to give up or negotiate for peace.
The main aim of Rheinübung was for the Bismarck to break into the Atlantic Ocean. Once there, it would attack Allied merchant ships carrying essential goods. The German Naval Command (OKM) set up a network of fuel tankers and supply ships. These ships were positioned along the route where the Bismarck and Prinz Eugen would sail. Britain knew that Nazi Germany planned to attack these supply lines. So, they sent many of their own ships, including battlecruisers, aircraft carriers, and battleships, to stop them.
Images for kids
-
Bismarck as seen from Prinz Eugen after the Battle of the Denmark Strait
See also
 In Spanish: Bismarck (1940) para niños
In Spanish: Bismarck (1940) para niños