Black bread mold facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Black bread mold |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Order: | Mucorales |
| Family: | Mucoraceae |
| Genus: | Rhizopus |
| Species: |
R. stolonifer
|
| Binomial name | |
| Rhizopus stolonifer Vuillemin (1902)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Rhizopus stolonifer is a common type of mold often called black bread mold. It belongs to a group of fungi called Zygomycota. This mold is found all over the world, especially in warm, humid places. It's well-known for causing food to spoil, like bread, fruits, and vegetables. R. stolonifer grows very quickly, especially indoors.
Contents
Discovering Black Bread Mold
This fungus was first found in 1818 by a German scientist named Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg. He called it Rhizopus nigricans. Later, in 1902, a French scientist named J. P. Vuillemin changed its name to Rhizopus stolonifer, which is what we call it today.
Where Black Bread Mold Lives
Rhizopus stolonifer lives almost everywhere on Earth. You can find it on many different types of moldy things. It's often one of the first molds to grow on old bread. This mold can live in soil and float in the air. It can grow on many natural surfaces because it can handle different amounts of nutrients. It uses various forms of carbon and nitrogen to grow.
In a lab, this fungus grows well on different food sources. These include those with ammonium salts or amino compounds. However, R. stolonifer cannot grow on Czapek's agar because it can't use nitrogen from nitrates. Rhizopus grows as tiny threads called hyphae and also as mature spores.
How Black Bread Mold Grows
This mold is a saprotroph, meaning it gets its food from dead or decaying matter. It helps break down materials in the soil. But it can also act as a parasite on plants, causing fruits and vegetables to rot. Like other Rhizopus species, R. stolonifer grows fast. It spreads using special runners called stolons. These stolons help the mold's body, called the mycelium, spread out and cover large areas. They can grow both up and across surfaces.
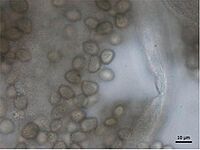
Rhizopus molds also produce root-like structures called rhizoids. These anchor the mold to its surface. They also grow unbranched stalks called sporangiophores. These stalks can be up to 2.5 millimeters long. The spores, which are like tiny seeds, can be different shapes. They might be oval, many-sided, or angled, depending on the food available. This mold grows best between 25 and 30 degrees Celsius. It can be killed at 60 degrees Celsius if kept at that temperature for ten minutes. Rhizopus stolonifer can even grow in acidic places, with a pH as low as 2.2. Its pH range for growth is from 2.2 to 9.6. Strong light, like ultraviolet light, can slow down when its spores start to grow.
How Black Bread Mold Reproduces
Rhizopus stolonifer can make new molds in two ways: without a partner (asexually) or with a partner (sexually). It is a heterothallic species, meaning it needs two different "mating types" to reproduce sexually. Sexual reproduction happens when two compatible types of mold threads (hyphae) meet. They then form special spores called zygospores. The stalks that hold the spores (sporangiophores) contain both '+' and '−' mating types within their spores. The process of meiosis, which mixes genetic material, happens when these zygospores sprout. The parts that form the zygospores, called gametogenia, can be different sizes. This size difference is usually because of how much food they get, not because of their "sex."
Black Bread Mold and Food Spoilage
This fungus mainly causes disease in ripe fruits like strawberries, melons, and peaches. These fruits are easily damaged and have more sugar, which the mold loves. R. stolonifer can also cause a soft rot in many vegetables, flowers, and seeds. After a few days, infected fruits become soft and release juices that smell a bit sour. If it's humid and warm, the mold grows quickly on the fruit's surface. It forms long, fuzzy runners with black spore cases, called sporangia, and spores.
When the fungus starts to grow, it makes special chemicals called esterases. One of these is cutinase, which helps the mold break through the plant's outer layer. Once the spores get inside, the mold releases other chemicals. These break down sugars like glucose and fructose. This process creates substances like fumaric acid, lactic acid, and ethanol. The mold can spread to other healthy fruits nearby. This happens when its spores are carried by wind or by insects.
To prevent this, some other fungi, like certain species of Syncephalis, can slow down R. stolonifer's growth. This can help stop or delay food spoilage after harvest. A natural anti-fungal substance called Fengycin can also kill the mold's cells. Treating sweet potatoes with certain chemicals like sodium orthophenyl phenol (Stopmold B) and dichloran (Botran W) has also helped reduce rot during storage.
In humans, Rhizopus stolonifer can sometimes cause infections. This usually happens in people who are already sick or have a weakened immune system. While rare, these infections can be serious. They might affect the lungs, sinuses, or ears. Breathing in mold spores from spoiled food could be one way people are exposed.
Why Black Bread Mold Matters
Rhizopus stolonifer is important in the economy because it causes a lot of food to spoil after harvest. This means farmers and stores lose money.
However, this mold also has some helpful uses! While yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is the main source for making industrial alcohol, R. stolonifer and other Rhizopus species can also produce ethyl alcohol. This is an important product made through fermentation. Rhizopus stolonifer is also used in factories to make pure fumaric acid and lactic acid. These acids are used in many products, including food and medicines. Interestingly, if there is zinc present, the mold makes less fumaric acid.
See Also
 In Spanish: Rhizopus stolonifer para niños
In Spanish: Rhizopus stolonifer para niños