Blue-headed macaw facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Blue-headed macaw |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Family: | Psittacidae |
| Genus: | Primolius |
| Species: |
P. couloni
|
| Binomial name | |
| Primolius couloni (P. L. Sclater, 1876)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The blue-headed macaw (Primolius couloni) is a beautiful parrot found in parts of Peru, Bolivia, and Brazil. It is also known as Coulon's macaw. This bird is about 41 centimeters (16 inches) long. This makes it one of the smaller macaws, sometimes called "mini-macaws." Like all macaws, it has a long, pointed tail and a strong, large beak.
The name couloni honors a Swiss scientist named Paul Louis Coulon.
Contents
What Does the Blue-headed Macaw Look Like?
The blue-headed macaw is mostly green. Its head, wing feathers, and the top parts of its wings are blue. The top of its tail is maroon at the base. It has a narrow green middle and a blue tip. The feathers under its tail and wings are yellowish-green. This is similar to other small macaws.
Its beak is medium-sized and light gray with a black base. Its eyes are whitish with a thin, dark red ring around them. Unlike most other macaws, the skin on its face and around its beak is dark gray. Its legs are a dull pink color.
Young blue-headed macaws look a lot like adults. However, their entire beak is black. They also have grayer legs and darker eyes. The skin on their face is white.
How Scientists Group This Macaw
Scientists group animals into different categories. The blue-headed macaw has been placed in different groups over time. Today, it is considered part of the Primolius group. Before, it was sometimes put in the Propyrrhura or Ara groups. The Ara group is now only used for larger macaws.
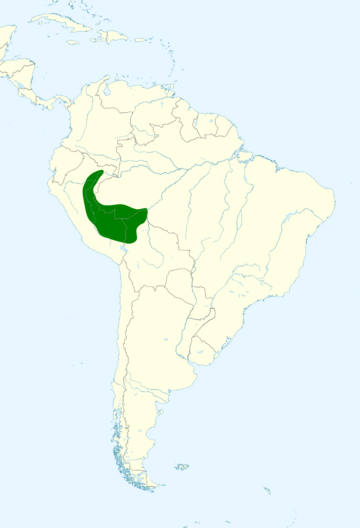
Where the Blue-headed Macaw Lives
This macaw lives in the southwestern Amazon Rainforest. It also lives in the nearby eastern Andean mountains. It likes open areas in humid forests. You can often find it along rivers or in clearings. It has also been seen in swamps and near towns.
Blue-headed macaws live from lowlands up to high altitudes. They can be found as high as 1,550 meters (5,100 feet). Like many other parrots, these macaws visit special places called clay-licks. They eat clay there, which helps them get important minerals.
Blue-headed Macaw Behavior and Life Cycle
Not much is known about how these macaws raise their young in the wild. People have seen possible nests in bamboo and tree holes. When kept by humans, they usually lay eggs once a year. A mother macaw typically lays 2 to 4 eggs.
In the wild, these birds are usually seen in small groups. They often fly in pairs or groups of 2 to 4. Sometimes, larger groups of up to 60 macaws have been seen. Their calls are higher-pitched and softer than most other macaws.
Protecting the Blue-headed Macaw
The blue-headed macaw was once thought to be common. However, studies in recent years showed it was rarer. Its total population is decreasing. Because of this, it is now considered a vulnerable species. This means it needs protection to survive. Some experts believe there might be more macaws than first thought.
Most of the forests where these macaws live are still healthy. But losing their habitat (their home) can be a problem in some areas. Luckily, they live in several protected places. These include Tambopata-Candamo and Manu National Park.
Another big problem for these birds is being captured. Some people catch them to sell as pets. This is illegal in many places. The price for these macaws can be very high. Many countries are working to stop this illegal trade. Zoos and special bird parks are also helping to protect them. They are trying to breed them so their numbers can grow.
See also
 In Spanish: Guacamayo cabeciazul para niños
In Spanish: Guacamayo cabeciazul para niños


