Boronia nana facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Dwarf boronia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Boronia nana var. hyssopifolia in Morton National Park | |
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
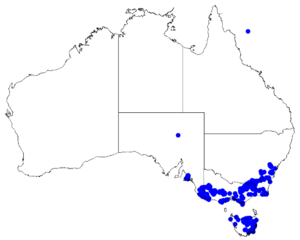
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium |
The Boronia nana, also known as the dwarf boronia or small boronia, is a special plant. It belongs to the citrus family called Rutaceae. This plant is endemic, meaning it only grows naturally in eastern Australia. It is a low-growing or spreading shrub. It has simple leaves or leaves made of three parts. Its pretty flowers are white or light pink and have four petals.
Contents
What Does Dwarf Boronia Look Like?
The Dwarf Boronia is a low-growing shrub. It can spread out or have weak branches that grow outwards. It usually grows to about 25 centimetres (10 inches) wide. It can reach up to 50 centimetres (20 inches) tall.
Its youngest branches have a few soft hairs. As they get older, they become smooth. The leaves can be simple (one part) or trifoliate (three parts). Each leaf or leaflet is shaped like a line, an oval, or an egg. They are usually 2 to 15 millimetres (0.08 to 0.6 inches) long. They are also 0.5 to 3.5 millimetres (0.02 to 0.14 inches) wide.
Dwarf Boronia Flowers
The flowers are white to pale pink. They grow alone or in small groups of up to three or more. These groups appear where the leaves join the stem (called leaf axils). Each group of flowers grows on a small stalk, 1 to 7 millimetres (0.04 to 0.3 inches) long. Each individual flower has its own tiny stalk, 2 to 16 millimetres (0.08 to 0.6 inches) long.
The flowers have four sepals, which are like small leaves that protect the bud. These sepals are triangular or broadly egg-shaped. They are 1 to 3.5 millimetres (0.04 to 0.14 inches) long. They are also 0.5 to 1.5 millimetres (0.02 to 0.06 inches) wide. Their bases overlap. The four petals are 3 to 5.5 millimetres (0.12 to 0.22 inches) long and 1.2 to 3 millimetres (0.05 to 0.12 inches) wide. Their bases also overlap. The stamens, which are the parts that produce pollen, are covered with long, soft hairs. Dwarf Boronia flowers bloom from October to February.
How Dwarf Boronia Got Its Name
The plant Boronia nana was first officially described in 1840. This description was made by a botanist named William Jackson Hooker. He published it in a book called Icones Plantarum. The plant he described was collected by Ronald Campbell Gunn at Rocky Cape National Park.
Scientists have recognized three different types, or varieties, of Boronia nana:
- Boronia nana var. hyssopifolia: This type has simple, single-part leaves.
- Boronia nana var. nana: This type mostly has leaves with three parts. Its leaves, sepals, and petals are mostly smooth (without hairs).
- Boronia nana var. pubescens: This type also mostly has leaves with three parts. However, its leaves have short, soft hairs.
Where Dwarf Boronia Grows
The different varieties of Dwarf Boronia grow in various parts of eastern Australia.
Where Boronia nana var. hyssopifolia Lives
This variety grows in woodlands, forests, and heathlands. It is the only type of B. nana found in New South Wales. There, it grows south of the Blue Mountains. You can also find it in central and eastern Victoria. It also grows in the far southeast of South Australia and the eastern half of Tasmania.
Where Boronia nana var. nana Lives
This variety prefers heathlands and heathy woodlands. It is mostly found in the south-west of Victoria. It also grows in the far south-east of South Australia.
Where Boronia nana var. pubescens Lives
This variety grows in rocky soils. It can be found in open forests, woodlands, and heathlands. It mainly grows between the Grampians and Lexton in Victoria. It is also found in the far south-east of South Australia.
Images for kids
-
Cyanothamnus nanus var. hyssopifolius photographed in Kosciuszko National Park



