Chromophore facts for kids
A chromophore is the part of a molecule that gives it its colour. Think of it as the "color-making" section of a tiny chemical structure.
The colour we see happens because the chromophore absorbs certain wavelengths of visible light. It then lets other wavelengths pass through or reflect off it. These unabsorbed wavelengths are the colours we actually see. For example, if a chromophore absorbs all colours except blue, then the object will look blue to us.
In living things, like plants or animals, chromophores are special parts of molecules that react when light hits them. They are key for things like capturing light energy (like in plants) or detecting light (like in our eyes).
Chromophores are found inside chromatophores. These are cells in many animals that contain pigments (the actual colour material) and can also reflect light. This is how animals like chameleons can change their skin colour!
Contents
What is a Chromophore?
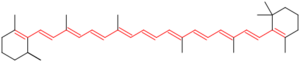
A chromophore is a specific group of atoms within a molecule. These atoms are arranged in a way that allows them to interact with light. When light energy hits these atoms, they can absorb some of it. The light that isn't absorbed is what our eyes see as colour.
How Do Chromophores Make Color?
Light is made of different wavelengths, and each wavelength corresponds to a different colour. For example, red light has a longer wavelength than blue light. A chromophore works by absorbing specific wavelengths of light. Imagine a sponge soaking up water; a chromophore "soaks up" certain colours of light. The colours that are not absorbed are either reflected or transmitted, and those are the colours we see. This is why a red apple looks red: its chromophores absorb all colours of light except red, which is reflected back to our eyes.
Chromophores in Nature
Chromophores are all around us and play a huge role in the natural world. They are responsible for the vibrant colours of flowers, the green of leaves, and the varied hues of animal skin and fur.
Why Leaves Change Color
One of the most common examples of chromophores at work is in leaves. During spring and summer, leaves are green because they contain a lot of a chromophore called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light, but reflects green light, making the leaves appear green.
As autumn arrives, the chlorophyll in leaves breaks down. When this green chromophore disappears, other chromophores that were always present in the leaf, like carotenoids (which make yellow and orange colours) and anthocyanins (which make red and purple colours), become visible. This is why leaves change into beautiful shades of yellow, orange, and red in the fall.
Images for kids
-
Leaves change color in the Fall because their chromophores (chlorophyll molecules) break down and stop absorbing red and blue light.
See also
 In Spanish: Cromóforo para niños
In Spanish: Cromóforo para niños


