Visible spectrum facts for kids
The visible spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that human eyes can see. We often call the energy in this range visible light or just light. It's what lets us see all the amazing colors around us!
Our eyes can usually see light with wavelengths from about 380 to 750 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a tiny unit of length, one billionth of a meter!
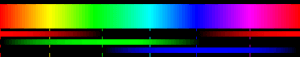
Think of a rainbow. It shows all the colors that come from a single wavelength of light. These are called pure spectral or monochromatic colors. But in real life, the colors in a rainbow blend smoothly into each other. There are no sharp lines between them.
What Colors Can We See?
| Color | Wavelength | Frequency | Photon energy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Violet | 380–450 nm | 668–789 THz | 2.75–3.26 eV |
| Blue | 450–495 nm | 606–668 THz | 2.50–2.75 eV |
| Green | 495–570 nm | 526–606 THz | 2.17–2.50 eV |
| Yellow | 570–590 nm | 508–526 THz | 2.10–2.17 eV |
| Orange | 590–620 nm | 484–508 THz | 2.00–2.10 eV |
| Red | 620–750 nm | 400–484 THz | 1.65–2.00 eV |
The table above shows the main colors we see in the visible spectrum. It also lists their typical wavelengths, frequencies, and photon energy.
- Wavelength is the distance between two peaks of a light wave. Shorter wavelengths are on the violet/blue end. Longer wavelengths are on the red end.
- Frequency is how many waves pass a point in one second. Higher frequency means shorter wavelength.
- Photon energy is the energy carried by a single particle of light (a photon). Higher energy means higher frequency and shorter wavelength.
How Do Screens Make Colors?
When you look at a computer screen or television, you're seeing colors made in a special way. These screens don't make every single color of the rainbow directly. Instead, they mix just three main colors: red, green, and blue.
By changing how much of each of these three colors they use, screens can create almost any color you can imagine. This is why these three are called "primary colors" for light. The image next to this text shows how different amounts of red, green, and blue are mixed to make the colors you see.
Images for kids
-
White light is split by a prism into the colors of the visible spectrum.
-
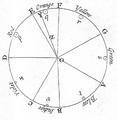
Isaac Newton's color circle from 1704. It shows how he linked colors to musical notes.
See also
 In Spanish: Espectro visible para niños
In Spanish: Espectro visible para niños