Cleopatra the Alchemist facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Cleopatra the alchemist
|
|
|---|---|

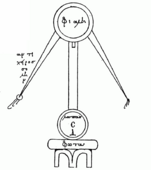
An old drawing of Cleopatra the Alchemist from a book called "Basilica philosophica" (1618).
|
|
| Born | c. 3rd century AD |
| Era | Ancient philosophy |
| Region | Western philosophy |
|
Main interests
|
Alchemy |
|
Notable ideas
|
Alembic |
|
Influences
|
|
Cleopatra the Alchemist (Greek: Κλεοπάτρα) was an important figure in alchemy. She was an alchemist, writer, and thinker who lived around the 3rd century AD.
Cleopatra worked on practical alchemy experiments. She is known as one of only four women alchemists who were believed to know how to make the Philosopher's stone. This was a legendary substance that could turn ordinary metals into gold. Some people also think she invented the alembic, which is a special tool used for distillation.
She was active in the ancient city of Alexandria. This was a big center for learning and science. She was part of a group of alchemists like Mary the Jewess and Comarius. These alchemists used complicated tools for their experiments.
Contents
Who Was Cleopatra the Alchemist?
Cleopatra the Alchemist is a pseudonym, which means it's a fake name. We don't know the real name of the person or group who wrote under this name. She is not the famous Egyptian queen, Cleopatra VII. However, some later books mistakenly called her Cleopatra, Queen of Egypt.
For example, in a book from 1618 called Basillica Philosophica, there's a picture of her "seal." It has a saying that means "God's secrets are hidden from people." She is also sometimes confused with another person named Cleopatra the Physician. Both lived around the same time and wrote in a similar style, using lots of grand pictures in their texts.
Cleopatra is also a character in some of the old alchemy writings. She appears in conversations within these texts.
What Did She Do for Alchemy?
Cleopatra was a very important early alchemist. She might have even lived before or at the same time as Zosimos of Panopolis, another famous alchemist. A writer named Michael Maier said she was one of four women who knew how to make the philosopher's stone. The others were Mary the Jewess, Medera, and Taphnutia.
She was highly respected in an Arabic encyclopedia from 988 called Kitab al-Fihrist. As mentioned, some people believe she invented the alembic. Cleopatra also tried to make alchemy more scientific. She worked with weights and measures to make experiments more exact.
Three alchemy texts are connected to Cleopatra. One is called A Dialogue of Cleopatra and the Philosophers. We don't know for sure if she wrote it. One expert, Jack Lindsay, called this text "the most imaginative and deeply felt document left by the alchemist."
Here are the names of the texts linked to her:
- On Weights and Measures (Greek: Ἐκ τῶν Κλεοπάτρας περὶ μέτρων καὶ σταθμῶν)
- Gold Making of Cleopatra (Greek: Χρυσοποιία Κλεοπάτρας)
- A Dialogue of the Philosophers and Cleopatra (Greek: Διάλογος φιλοσόφων καὶ Κλεοπάτρας)
Cleopatra used many pictures and symbols in her writings. These often showed ideas of birth, new life, and changing things. She compared an alchemist working on their experiments to a loving mother caring for her child.
The Chrysopoeia of Cleopatra
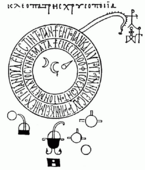
Cleopatra is most famous for the Chrysopoeia of Cleopatra. This name means "gold-making" in Greek. It's a special document that has only symbols, drawings, and short descriptions.
The original document is on a single page. It was found in a very old book from the 10th or 11th century. This book is kept in a library in Venice, Italy. Another copy is in Leiden University in the Netherlands.
One famous drawing in the Chrysopoeia is the serpent eating its own tail. This symbol is called the Ouroboros. It means that everything is connected, and that the beginning is also the end, and the end is the beginning. It represents unity and eternity.
Around the Ouroboros, there's a message in a double ring. It says:
One is the Serpent which has its poison according to two compositions, and One is All and through it is All, and by it is All, and if you have not All, All is Nothing.
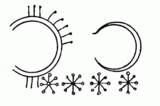
Inside this ring, there are also symbols for gold, silver, and mercury. There are drawings of two alchemy tools: a "dibikos" and a "kerotakis." Another symbol she used is an eight-pointed star. People believe the star and crescent moon shapes next to it show how lead could be turned into silver.
See also
 In Spanish: Cleopatra la Alquimista para niños
In Spanish: Cleopatra la Alquimista para niños