Ouroboros facts for kids
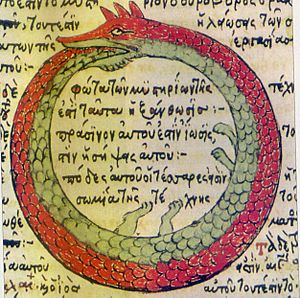
The ouroboros (say: oh-roo-BOH-ros) is a very old symbol. It shows a snake or a dragon eating its own tail. This symbol stands for a never-ending cycle, like life, death, and then new life starting again.
It means that something is always creating itself over and over. Think of it like the phoenix, a mythical bird that burns up and is reborn from its own ashes. The ouroboros shows cycles that finish and then immediately begin again.
Contents
The Ouroboros Symbol
What the Ouroboros Means
The ouroboros is a powerful symbol. It often means eternity, which is forever. It also means things that happen in a cycle, repeating over and over. It shows how the end of one thing can be the start of another.
This symbol helps us think about how life keeps going. It reminds us that even when something ends, new things can begin. It's a way to show that everything is connected in a big, never-ending loop.
History of the Ouroboros
The first known picture of the ouroboros was found in KV62. This is the tomb of Tutankhamun, an ancient Egyptian pharaoh. This tomb was built around 1400 BC.
The pictures in the tomb tell a story about the god Ra and his journey. In one drawing, two snakes are shown. They have their tails in their mouths, wrapping around a huge god. This god is a mix of Ra and another god, Osiris. This whole picture shows the start and end of time.
The ouroboros symbol has appeared in many different cultures. It has been seen in ancient Egypt, Greece, and even in Norse mythology. It also became important in alchemy, which was an old form of chemistry. Alchemists used it to show how things can change and transform.
Images for kids
-
The first known ouroboros, found on a shrine in Tutankhamun's tomb.
-
A very fancy ouroboros from The Book of Kells, an old book made around 800 CE.
See also
 In Spanish: Uróboros para niños
In Spanish: Uróboros para niños