Computer data storage facts for kids
Computer data storage is a way for computers to keep information. It's like a computer's memory or a digital filing cabinet. Its main job is to store data so the central processing unit (CPU) can use it. The CPU can then read or change this data whenever it needs to.
Computers have different types of storage, arranged in a "memory hierarchy." This means some storage is very fast but small, while other storage is slower but much bigger. Storage that is closer to the CPU is usually faster. This fast storage often needs power to keep the data.
Storage that is farther away from the CPU is usually slower but can hold a lot more data. Think of hard drives or USB flash drives. Some storage can hold even more, like tape drives, but it's very slow to get data from them.
Contents
What is Primary Storage?
Primary storage is the fastest type of memory. The CPU can access it directly and very quickly. This is where the computer keeps data it is actively using right now.
- CPU Registers: These are tiny, super-fast storage areas right inside the CPU. They hold data that the CPU is working on at that exact moment.
- Cache Memory: This is a small, very fast memory that stores copies of data from main memory. It helps the CPU get data even faster, as it doesn't have to go all the way to the main memory every time.
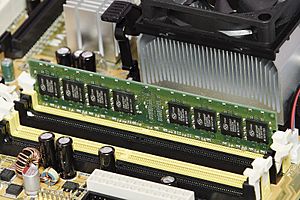
- Main Memory (RAM): This is often called RAM. It's where the computer stores programs and data that are currently running. When you turn off the computer, most data in RAM disappears.
What is Secondary Storage?
Secondary storage is where computers keep data for a longer time. Unlike primary storage, the CPU usually can't access secondary storage directly. Data from here needs to be moved to primary storage (RAM) before the CPU can use it.
- Hard Drives: These are common examples of secondary storage. They can store large amounts of data, like your operating system, programs, and files.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): These are newer, faster types of drives that store data on flash memory chips. They are often used in modern computers and laptops.
- USB Flash Drives: These are small, portable devices you can plug into a computer to store and carry files.
What is Tertiary Storage?
Tertiary storage is used for very large amounts of data, often for backups or archiving. It's usually the slowest type of storage. Data from tertiary storage is often copied to secondary storage before it can be used.
- Magnetic Tapes: These are like old-fashioned cassette tapes but for computer data. They can store huge amounts of information and are often used by big companies for long-term backups.
- Optical Discs: These include CD-ROMs and DVDs. They were once common for distributing software and movies.
Images for kids
-
This is a 160 GB SDLT tape cartridge. It's an example of off-line storage.
-
A hard disk drive with its protective cover removed.
-
A software warning from S.M.A.R.T. This means the hard drive might fail soon.
-
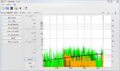
This graph shows the error rate on a DVD+R disc. The small errors can be fixed.
See also
 In Spanish: Memoria (informática) para niños
In Spanish: Memoria (informática) para niños