Crankshaft facts for kids
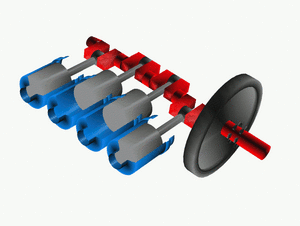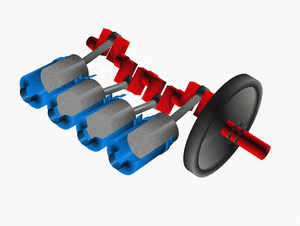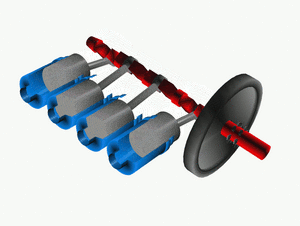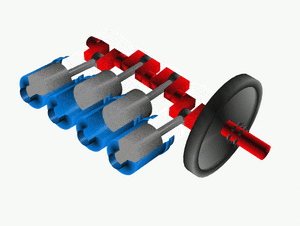
The crankshaft is a super important part of many engines, like those in cars, boats, and even some airplanes! You can think of it as the engine's "spine" or "backbone." Its main job is to turn the up-and-down movement of parts called pistons into a spinning motion. This spinning motion is what eventually makes wheels turn or propellers spin.
To do this, the crankshaft has special offset parts, like little arms. The pistons are connected to these arms. When a piston moves up and down, it pushes on its arm, which then forces the entire crankshaft to spin.
Smoothing the Ride
When pistons push, they create a bit of a jerky, pulsing motion. To make the spinning smoother, a crankshaft is usually connected to a heavy wheel called a flywheel. The flywheel acts like a balancer, helping to keep the rotation steady and even.
Sometimes, there's also a special part called a vibration damper on the other end of the crankshaft. This damper helps to reduce any shaking or vibrations that the crankshaft might create while it's working.
Why More Cylinders are Better
Large engines, like those in big trucks or ships, usually have many cylinders and pistons. Having more pistons helps to make the engine's power delivery much smoother. Instead of just one big push, you get many smaller, overlapping pushes, which reduces the jerky feeling.
Some crankshafts also have special weights called counterweights. These weights help to balance the movement of the pistons. Even though counterweights add extra weight to the crankshaft, they make the engine run much more smoothly. This smoothness allows the engine to spin faster (reach higher RPMs) and produce more power!
Images for kids
-
15th century paddle-wheel boat whose paddles are turned by single-throw crankshafts (Anonymous of the Hussite Wars)
-
Crankshaft, pistons and connecting rods for a typical internal combustion engine
See also
 In Spanish: Cigüeñal para niños
In Spanish: Cigüeñal para niños
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |