Cyanosis facts for kids
|
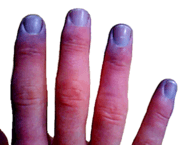
Cyanosis of the fingertips and nail beds.
|
|
| ICD-10 | R23.0 |
|---|---|
| ICD-9 | 782.5 |
| eMedicine | med/3002 |
Cyanosis is a medical sign where a person's skin and mucous membranes turn blue or purple. Mucous membranes are the moist linings inside your body, like in your mouth or nose. This color change happens when the blue or purple parts of the body are not getting enough blood and oxygen.
This can happen for a few reasons. Sometimes, there isn't enough oxygen in the blood itself. Other times, tiny blood vessels in the body get smaller. This narrowing of blood vessels is called vasoconstriction.
Where Does Cyanosis Show Up?
Cyanosis usually appears first in the parts of the body farthest from the heart. These areas are called the extremities. You might first notice it on the fingertips (especially under the fingernails), toes, lips, the tip of the nose, or earlobes.
As the body goes longer without enough oxygen, more areas can start to look blue or purple. It's a sign that something is wrong and needs medical attention.
Images for kids
-
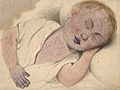
Child with congenital heart disease with central cyanosis that is worsened by measles. Note the bluish-purple discoloration of the fingernails, lips, eyelids, and nose, along with prominent nail clubbing.
-
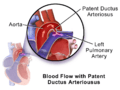
Initial direction of blood flow in patients with patent ductus arteriosus. Once the pressure of the pulmonary arteries increases more than the aorta due to right heart hypertrophy, the direction of blood flow reverses, sending deoxygenated blood through the patent duct directly into the descending aorta while sparing the brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid, and left subclavian artery, therefore causing the differential cyanosis.
See also
 In Spanish: Cianosis para niños
In Spanish: Cianosis para niños