Declination facts for kids
Declination is a special way astronomers use to find things in space. Imagine a giant map of the sky. Declination helps you know how far north or south a star or planet is on that map. It's a lot like latitude on Earth, which tells you how far north or south a city is from the equator.
Contents
What is Declination?
Declination (often shortened to dec or δ) is one of the main "addresses" for objects in space. Think of it as a coordinate, like the numbers you use to find a spot on a treasure map. Astronomers use it to pinpoint the exact location of stars, planets, and galaxies.
Declination and the Celestial Sphere
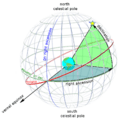
Imagine Earth is at the center of a huge, imaginary ball called the celestial sphere. All the stars and planets appear to be stuck on the inside of this ball. The celestial sphere is a helpful tool for understanding where things are in the sky.
Just like Earth has an equator, the celestial sphere has a celestial equator. This is an imaginary line that circles the sky directly above Earth's equator.
How is Declination Measured?
Declination tells you how far an object is from the celestial equator. It is measured in degrees.
- If an object is north of the celestial equator, its declination is a positive number.
- If an object is south of the celestial equator, its declination is a negative number.
The numbers range from +90 degrees (at the celestial north pole) to -90 degrees (at the celestial south pole). The celestial equator itself is at 0 degrees declination.
Declination and Latitude
Declination is very similar to latitude on Earth. Latitude tells you how far north or south a place is from Earth's equator. Declination does the same thing for objects in the sky, but on the celestial sphere.
For example, if you are at the North Pole on Earth, you are at 90 degrees north latitude. From there, the celestial north pole would be directly overhead.
Finding Objects in Space
Declination is one of two coordinates used in the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is called right ascension.
- Declination tells you how far north or south an object is.
- Right ascension tells you how far east or west an object is.
Together, these two coordinates give astronomers a precise way to locate anything in the night sky. It's like using street numbers (declination) and street names (right ascension) to find a house.
Knowing an object's declination helps scientists track its movement and predict where it will be in the future. This is important for things like launching spacecraft or observing distant galaxies.
Images for kids
-
Right ascension (blue) and declination (green) as seen from outside the celestial sphere.
-
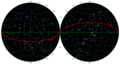
The night sky, divided into two halves. Declination (blue) begins at the equator (green) and is positive northward (towards the top), negative southward (towards the bottom). The lines of declination (blue) divide the sky into small circles, here 15° apart.
See also
 In Spanish: Declinación (astronomía) para niños
In Spanish: Declinación (astronomía) para niños
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |