Diabetes facts for kids
- There is another type of diabetes, called diabetes insipidus
Diabetes is a health condition. It happens when your body has trouble using glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar that your body uses for energy.
Your body gets glucose from the food you eat. A special chemical called insulin helps glucose get into your cells. Insulin is a hormone made by an organ called the pancreas.
When you eat, your pancreas releases insulin. Insulin tells your body's cells to take in glucose from your blood. This glucose then gives your cells energy. If there's extra glucose, your body stores it for later.
If your body doesn't make enough insulin, or if the insulin it makes doesn't work well, glucose stays in your blood. This can cause health problems. When people say "diabetes," they usually mean diabetes mellitus. People with this condition are called "diabetics."
Contents
Types of Diabetes
|
|
|---|
The onset of symptoms in Type 1 diabetes usually happens suddenly. In Type 2 diabetes, there may be mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. Making it much harder to detect. |
There are different types of diabetes. Each type affects how your body handles glucose in a different way.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes happens when your body's own immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas. These are the cells that make insulin. Because the pancreas can't make insulin, glucose can't get into your body's cells.
People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin every day. They need to check their blood sugar levels often. This type of diabetes usually starts in younger people. About 1 in 10 people with diabetes have Type 1.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is different from Type 1. In Type 2, your body still makes insulin. But either it doesn't make enough, or the insulin doesn't work as it should. This means glucose can't get into your cells properly.
Type 2 diabetes often develops in older people. It is also more common in people who are overweight.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is similar to Type 2 diabetes. It can happen to some women when they are pregnant. It usually goes away after the baby is born.
Other Types of Diabetes
There are also other less common types of diabetes. These include:
Diabetes Complications
Complications are health problems that can happen because of a disease. With diabetes, there are two main kinds of complications.
Acute complications happen quickly. They are often caused by blood glucose levels being too high or too low.
- High blood glucose (called hyperglycemia) can be very dangerous. In Type 1 diabetes, it can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. This is a serious condition that needs urgent medical help. You might notice a fruity smell on the breath.
- Low blood glucose (called hypoglycemia) can also be dangerous. If your blood sugar drops too much, you might sweat, tremble, or feel confused. You could even pass out. Eating something with sugar can help quickly. Sometimes, a special medicine called 'glucagon' is given. Hypoglycemia usually happens if someone takes too much diabetes medicine, doesn't eat enough, or exercises too much.
Chronic complications (or long-term complications) develop over many years. They are caused by blood glucose levels being too high for a long time. This can damage your blood vessels and nerves.
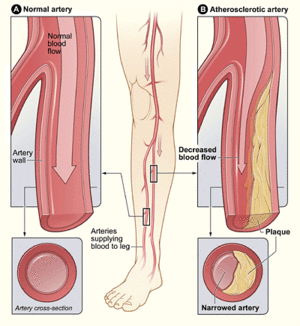
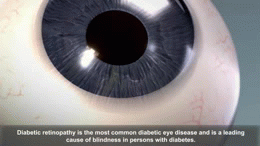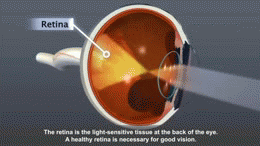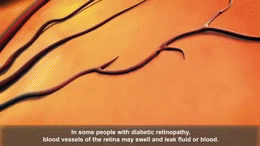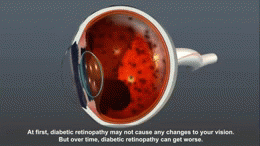
- Damage to blood vessels can lead to serious issues. These include strokes, heart attacks, kidney failure, and blindness. It can also cause wounds to heal slowly. Sometimes, poor blood flow can even lead to amputations, especially in the feet.
- Damage to nerves can make it hard to feel pain, often in the feet. This means injuries might go unnoticed. Nerve damage can also cause pain even when there's no injury. This is sometimes called "ghost pain."
Monitoring Diabetes
Because high blood glucose can cause problems, it's important to treat diabetes. The main goal is to keep blood glucose levels as normal as possible. A normal range is usually 80-120 mg/dL.
People with diabetes should check their blood glucose often. They use a small device called a glucometer. This helps them know if their blood sugar is too high or too low. Many people check their blood sugar several times a day.
Doctors also use a blood test called hemoglobin A1C (or Hgb-A1C). This test shows what the average blood glucose level has been for the past 90 days. It helps doctors decide if changes to diet or medicine are needed.
Regular check-ups are important to watch for complications. People with diabetes should see an eye doctor often to check for eye damage. They also need to check their feet daily for cuts or sores. Doctors will check their kidneys and nerves too.
Treating Diabetes
The most important part of treating diabetes is keeping blood glucose levels close to normal. This often takes careful planning. Treatment can be different for Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- People with Type 1 diabetes are treated with insulin.
- People with Type 2 diabetes often start with changes to their diet, more exercise, and weight loss. Sometimes, they also need medicine or insulin.
Learning about diabetes is very important. People with diabetes learn about healthy eating. They learn how to count carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in their food. This helps them plan meals with the right balance. For Type 1 diabetes, knowing what you eat helps decide how much insulin to take.
Exercise is also important for health. But people with diabetes must plan their exercise carefully. Too much intense exercise can sometimes cause low blood sugar.
Besides controlling blood glucose, other treatments may be needed. People with diabetes often have a higher risk of blood vessel problems. So, it's extra important to manage other conditions that affect blood vessels. For example, treating high blood pressure and high cholesterol is very important for diabetics. These conditions can also damage blood vessels.
Images for kids
-
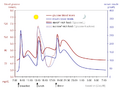
The fluctuation of blood sugar (red) and the sugar-lowering hormone insulin (blue) in humans during the course of a day with three meals. One of the effects of a sugar-rich vs a starch-rich meal is highlighted.
See also
 In Spanish: Diabetes mellitus para niños
In Spanish: Diabetes mellitus para niños
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |