Dimorphic fungus facts for kids
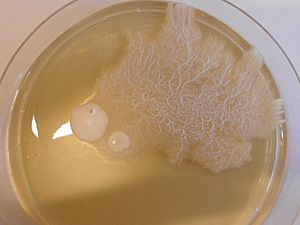
Dimorphic fungi are special types of fungi. They have an amazing ability to exist in two different forms: as a fuzzy mold or as tiny, single-celled yeast. This change in form usually happens because of a change in temperature. That's why they are also known as thermally dimorphic fungi.
For example, a fungus called Talaromyces marneffei grows as a mold when it's at regular room temperature. But if it gets into a human body, where it's much warmer (at human body temperature), it changes into a yeast!
The word "dimorphic" means "having two forms." While these fungi are known for switching between mold and yeast, some can actually take on even more shapes. So, "dimorphic" is often used as a general term for fungi that can switch between these two main forms.
Where Do Dimorphic Fungi Live?
Many dimorphic fungi are important because they can cause infections in humans and other animals. Some well-known examples include Coccidioides immitis, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, Candida albicans, Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Sporothrix schenckii, and Emmonsia species.
These fungi can cause different types of infections, such as:
- sporotrichosis
- blastomycosis
- histoplasmosis
- coccidioidomycosis
- paracoccidioidomycosis
- talaromycosis
- candidiasis
Not all dimorphic fungi cause disease. Some are found in plants, like Ustilago maydis, which affects corn. Others are even used by people, such as Geotrichum candidum, which helps make cheese!
How to Remember Dimorphic Fungi
In medical studies, students use fun memory tricks, called mnemonics, to remember how these fungi change form based on temperature.
Here are some popular ones:
- Mold in the Cold, Yeast in the Heat (like a Beast)
- This helps you remember that many of these fungi are molds in cooler temperatures and yeasts in warmer temperatures.
- Body Heat Probably (Changes) Shape
- This mnemonic helps you remember specific fungi that change in the heat:
- Blastomyces dermatitidis
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
- Coccidioides immitis (This one is a bit different; it changes into a special sphere of spores, not exactly yeast, in the heat.)
- Sporothrix schenckii
- This mnemonic helps you remember specific fungi that change in the heat:
Remember, the word "Probably" is in the mnemonic because there's always an exception! For example, Candida albicans is a dimorphic fungus that actually changes in the opposite way: it can grow as mold-like structures when it's warm!
See also
 In Spanish: Dimorfismo fúngico para niños
In Spanish: Dimorfismo fúngico para niños